diff --git a/docs/.nojekyll b/docs/.nojekyll
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e69de29
diff --git a/docs/README.md b/docs/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..906fe8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+### Tutorial Content
+
+The tutorial has been designed to be followed along, so you could start from the beginning through the end. At the end of each lesson, there will be a link to the whole code on GitHub.
+
+> __Note__
+> If you're using Bootstrap 3 CSS, clone the code from [vuetable-2-tutorial-bootstrap](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial-bootstrap) instead.
+>
+> If you're using Bulma CSS, clone the code from [vuetable-2-tutorial-bulma](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial-bulma).
+
+
+##### Prerequisite
+- [Install the required tools](./prerequisite#install-the-required-tools)
+- [Create a tutorial project with Vue-CLI](./prerequisite#create-a-tutorial-project-with-vue-cli)
+- [Sample API endpoint](./prerequisite#sample-api-endpoint)
+
+##### Lessons
+1. [Your first Vuetable](./lesson-01)
+2. [Displaying more fields](./lesson-02)
+3. [Cleaning up code](./lesson-03)
+4. [Make change to field title](./lesson-04)
+5. [Column alignment](./lesson-05)
+6. [Format fields using `callback` option](./lesson-06)
+7. [Adding pagination](./lesson-07)
+8. [Displaying pagination information](./lesson-08)
+9. [Customizing Vuetable](./lesson-09)
+10. [Make columns sortable](./lesson-10)
+11. [Using special fields](./lesson-11)
+12. [Adding Detail Row](./lesson-12)
+13. [Adding Search Filter](./lesson-13)
+
+14. [Moving Field Definitions to another file](./lesson-14)
+15. [Passing Props to MyVuetable - Part 1](./lesson-15)
+16. [Passing Props to MyVuetable - Part 2](./lesson-16)
+17. [Passing Scoped Slot to MyVuetable](./lesson-17)
+18. Converting to Bootstrap CSS
+ - The `css` property
+ - Table Styling
+ - Pagination Styling
+ - Using the `icon-render` property
+
+##### Contributions
+
+You can PR on any error you've encountered. No matter you think how small it is, please do not worry. :)
diff --git a/docs/_sidebar.md b/docs/_sidebar.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6b31dec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/_sidebar.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+#### [Tutorial Content](./Home)
+
+##### Prerequisite
+- [Install the required tools](./prerequisite#install-the-required-tools)
+- [Create a tutorial project with Vue-CLI](./prerequisite#create-a-tutorial-project-with-vue-cli)
+- [Sample API endpoint](./prerequisite#sample-api-endpoint)
+
+##### Lessons
+- [Your first Vuetable](./lesson-01)
+- [Displaying more fields](./lesson-02)
+- [Cleaning up code](./lesson-03)
+- [Make changes to field titles](./lesson-04)
+- [Column alignment](./lesson-05)
+- [Format fields using `callback` option](./lesson-06)
+- [Adding pagination](./lesson-07)
+- [Displaying pagination information](./lesson-08)
+- [Customizing Vuetable](./lesson-09)
+- [Make columns sortable](./lesson-10)
+- [Using special fields](./lesson-11)
+- [Adding Detail Row](./lesson-12)
+- [Adding Search Filter](./lesson-13)
+- [Moving Field Definitions to another file](./lesson-14)
+- [Passing Props to MyVuetable - Part 1](./lesson-15)
+- [Passing Props to MyVuetable - Part 2](./lesson-16)
+- [Passing Scoped Slot to MyVuetable](./lesson-17)
diff --git a/docs/index.html b/docs/index.html
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..557e24f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/index.html
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+
+
+
+
+ vuetable-2-tutorial - A Vue.js project
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs/lesson-01.md b/docs/lesson-01.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..7eb890c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-01.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+# Your first Vuetable
+
+* install `babel-preset-es2015` via yarn
+ ```shell
+ $ yarn add babel-preset-es2015 --dev
+ ```
+
+ This is necessary because we're going to use ES2015 syntax in our code.
+
+* install vuetable-2 using yarn
+
+ ```shell
+ $ yarn add vuetable-2 --dev
+ ```
+
++ Create MyVuetable component (`src\components\MyVuetable.vue`)
+
+ ```vue
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```
+
++ Modify `index.html` to include [JQuery] and [Semantic UI]
++
+ ```html
+
+
+
+
+ vuetable-2-tutorial
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```
+
++ Modify `App.vue` to use `MyVuetable` component instead of `Hello` component
+
+ ```html
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```
+
+* Run the project to see the changes`
+ ```shell
+ $ yarn run dev
+ ```
+
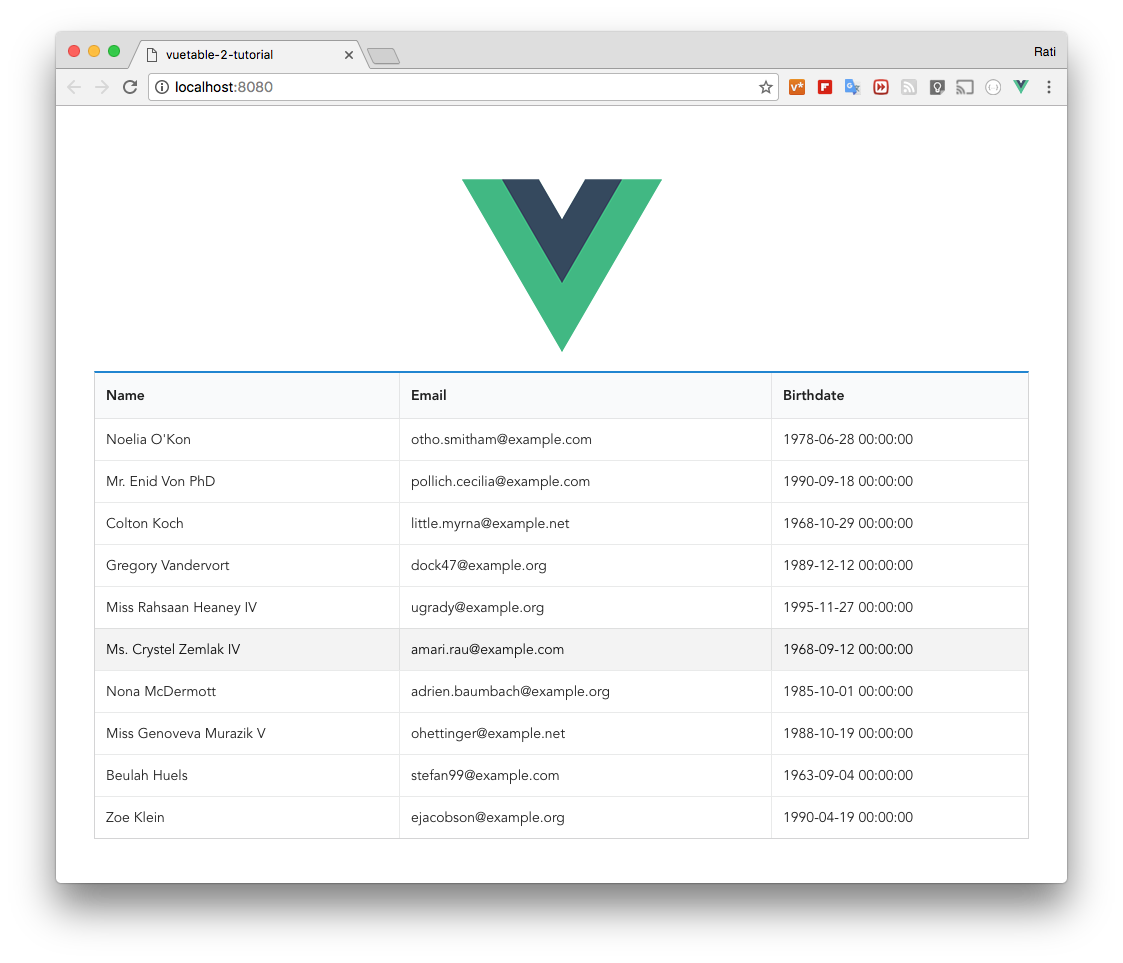
+ you should see something like this
+
+ 
+
+### Congratulations!
+
+You've now successfully created your first component using Vuetable.
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-1)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-02.md b/docs/lesson-02.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..22aecc9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-02.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+# Displaying more fields
+
+## Add more fields to MyVuetable
+Looking at the sameple data from the API, we have more information that we could display especially the data in the `address` object.
+
+Let's see how we can display those nested data
+
+* add `address.line1`, `address.line2`, `address.zipcode` in `MyVuetable.vue`
+
+ ```vue
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ ```
+
+* run the project
+
+ ```shell
+ $ yarn run dev
+ ```
+
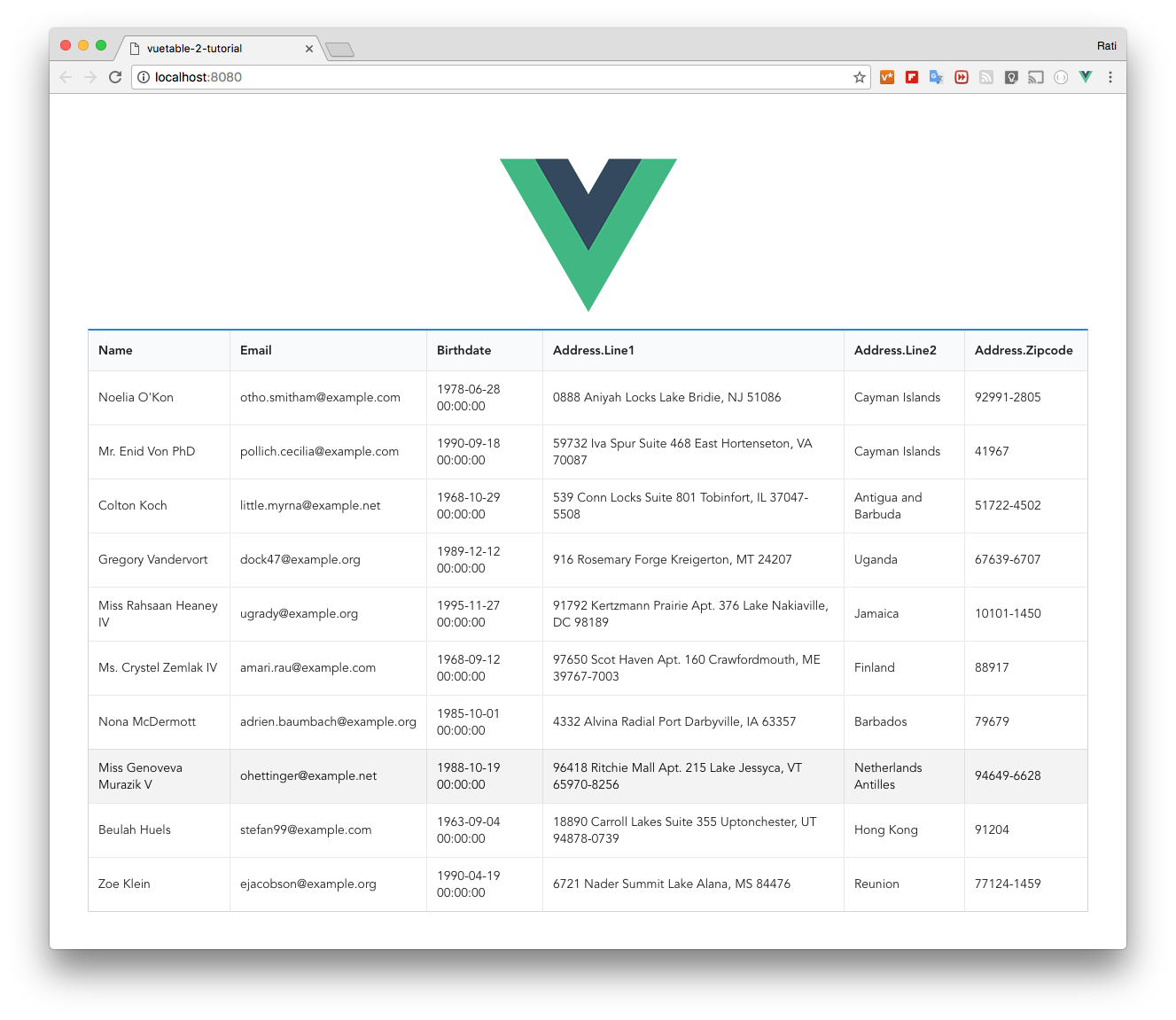
+ You should now see the additional fields showing in our Vuetable
+ 
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-2)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-03.md b/docs/lesson-03.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..de7464f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-03.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+
+# Cleaning up code
+
+In the last lesson, we added more fields to be displayed using the `fields` prop. In the more complex data structure, there could be a lot more field to display. As you can see the `fields` prop could get quite lengthy.
+
+We could make use of the `data` section of Vue to make it cleaner, like so.
+
+```vue
+// MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+Run the project again to see that everything is still working the same.
+```shell
+ $ yarn run dev
+```
+
+We should also remove the unused file that comes pre-install with vue-cli webpack template.
+- Delete `src\components\Hello.vue`
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-3)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-04.md b/docs/lesson-04.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..06536bb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-04.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+# Make change to field title
+
+By default, vuetable uses the field name as column title in the table header. But we could easily change it to whatever we want.
+
+Let's look at how we can change the titles for address related columns.
+
+```vue
+// MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+The `fields` prop will internally get converted by Vuetable to an array of **field definition object**.
+
+Each field definition object contains other options that will allow Vuetable to do much more. In this lesson, we only use `title` option to change the column title.
+
+As you can see, we can mix `string` and `object` in the field definition. Those `string` will be used as `name` option of field definition when they are converted to object.
+
+Later, we will learn about other options of field definition object that could combine those address into one column or hide it until it's needed to be displayed.
+
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-4)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-05.md b/docs/lesson-05.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8a158e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-05.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+# Column alignment
+
+Let's make some adjustments to the `MyVuetable.vue` by removing and adding some fields.
+
+- remove following fields: `address.line1`, `address.line2`, and `address.zipcode`
+- then, add these fields: `nickname`, `gender`, and `salary`
+
+Your code should look like this
+
+```vue
+// MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+Now, you can specify the appropriate CSS class for column alignment.
+
+- Sementic UI
+ - class="left aligned"
+ - class="center aligned"
+ - class="right aligned"
+
+- Bootstrap 3
+ - class="text-left"
+ - class="text-center"
+ - class="text-right"
+
+`titleClass` option is used to specify the alignment of the field title.
+
+`dataClass` option is used to specify the alignment of the field data.
+
+We will add these options to `birthdate`, `gender`, and `salary` fields.
+
+```vue
+// MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
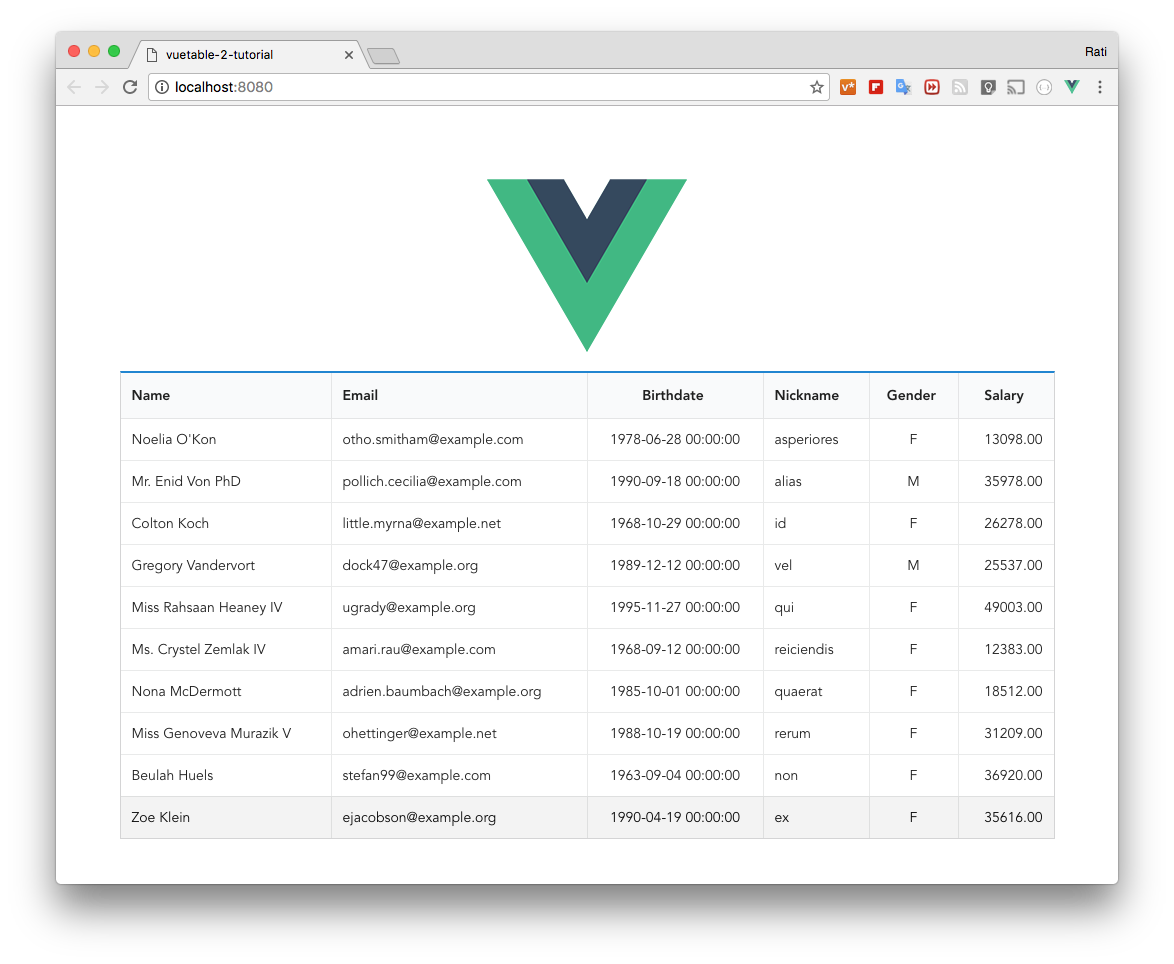
+Run the project and you should see this
+
+
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-5)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-06.md b/docs/lesson-06.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..5f059aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-06.md
@@ -0,0 +1,278 @@
+# Format fields using `callback` option
+
+In this lesson, we will use `callback` option of Vuetable to format the following fields
+
+* `nickname` -- display in all upppercase letters
+* `gender` -- display `Male` or `Female` as colored label with an icon
+* `salary` -- using [accounting.js](http://openexchangerates.github.io/accounting.js) to display the value with thousand separator
+* `birthdate` -- using [moment.js](https://momentjs.com/) to display different date format
+
+The `callback` option allows us to specify the callback function for a specific field to handle the value of the column data to be displayed. Vuetable will use the returned value of the callback to display the data in that column.
+
+## `nickname` field
+Let's begin with displaying `nickname` in all upppercase.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //...
+ {
+ name: 'nickname',
+ callback: 'allcap'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ },
+ methods: {
+ allcap (value) {
+ return value.toUpperCase()
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+The `callback` option of `nickname` field specifies that the value of `nickname` should be handle by the callback function named `allcap` defined in this component/instance.
+
+So, we then define the `allcap` function in the `methods` block of the component. The `callback` function will recieved 2 parameters from Vuetable, which are
+
+* the `value` of the column data in the current row
+* and, additional parameter string
+
+In this case, we only use the first parameter (`value`). We will see the use of the second parameter later when we create a callback function for `birthdate` field.
+
+## `gender` field
+Now, we will make use of the CSS framework to format the gender field to display the icon label.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //..
+ {
+ name: 'gender',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'center aligned',
+ callback: 'genderLabel'
+ },
+ //..
+ ]
+ }
+ },
+ methods: {
+ //...
+ genderLabel (value) {
+ return value === 'M'
+ ? 'Male'
+ : 'Female'
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+As you can see, returned value of the callback function can also be a valid HTML. So, you can freely use any CSS framework that you like to style it.
+
+Here is example of using Bootstrap 3:
+
+```javascript
+ //...
+ genderLabel (value) {
+ return value == 'M'
+ ? ' Male'
+ : ' Female'
+ }
+```
+
+## `salary` field
+To format the `salary` field, we will use `formatNumber` function of [`accounting.js`](http://openexchangerates.github.io/accounting.js/) library to do the job.
+
+First let's include the `accounting.js` using `yarn`
+```shell
+ $ yarn add accounting --dev
+```
+
+> We are using original accounting.js library, which is named `accounting`. There are other similar packages, you can pick the one the you like.
+
+
+Now, we have to import it into MyVuetable before we can use it.
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+```
+
+Add the `callback` option to `salary` field definition
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //...
+ {
+ name: 'salary',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'right aligned',
+ callback: 'formatNumber'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ },
+```
+
+Then, define `formatNumber` function in the `methods` block
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ methods: {
+ //...
+ formatNumber (value) {
+ return accounting.formatNumber(value, 2)
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+## `birthdate` field
+To format date, we will use [`momentjs`](https://momentjs.com/) to do this.
+
+We have to include `momentjs` library first using `yarn`
+```shell
+$ yarn add moment --dev
+```
+> The NPM package for `momentjs` is named `moment`
+
+Let's import the `momentjs` to be use inside the MyVuetable.vue.
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+```
+
+Add the `callback` option to `birthdate` fiel definition
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //...
+ {
+ name: 'birthdate',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'center aligned',
+ callback: 'formatDate|DD-MM-YYYY'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+And, define `formatDate` function in the `methods` block
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ methods: {
+ //...
+ formatDate (value, fmt = 'D MMM YYYY') {
+ return (value == null)
+ ? ''
+ : moment(value, 'YYYY-MM-DD').format(fmt)
+ }
+ }
+```
+
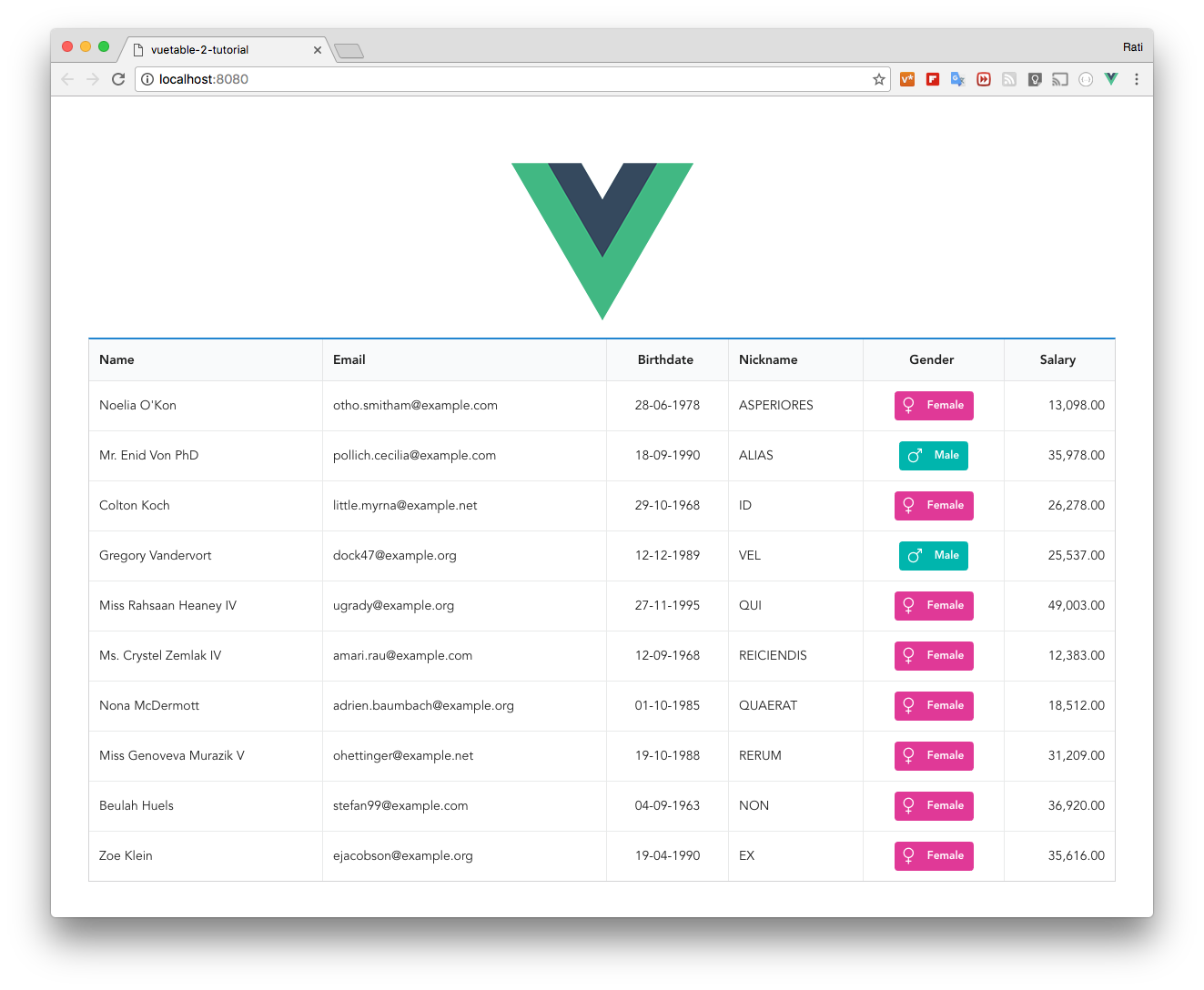
+
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-6)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-07.md b/docs/lesson-07.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..109e9e5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-07.md
@@ -0,0 +1,361 @@
+# Adding pagination
+
+So far, we have just only display the first page of data. In this lesson, we'll add table pagination to our Vuetable.
+
+### Pagination components
+Vuetable already have two ready-to-use pagination components, [`VuetablePagination`](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/blob/master/src/components/VuetablePagination.vue) and [`VuetablePaginationDropdown`](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/blob/master/src/components/VuetablePaginationDropdown.vue).
+
+These two pagination components are only different in the appearance. Most of the functionality are the same because they both use [`VuetablePaginationMixin`](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/blob/master/src/components/VuetablePaginationMixin.vue) mixin, which provides pagination related functions.
+
+That means you can also write your own pagination component with ease by just providing the template that uses available functions in the mixin.
+
+> In the [first version](https://github.com/ratiw/vue-table) of Vuetable, pagination is part of the Vuetable template. This makes it easy to begin with, but also makes it inflexible if you want to customize it. That's why the pagination component is not embedded into Vuetable-2 by default.
+
+Now, let's put the pagination component in our MyVuetable template.
+
+```vue
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+However, this won't work just yet because Vue would throw a compilation error at you if you run it. The error would be something similar to this.
+
+```shell
+ template syntax error Component template should contain exactly one root element.
+```
+> __Note__
+> The error message might vary a little bit from different version of Vue
+
+Vue now requires that your component has only one root and if it doesn't, it will throw the above error message.
+
+To fix this, you just have to wrap those components in one HTML tag like `` like this.
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
// <---
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+But if you look at the template in `App.vue`, you should see that we have `
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+And, modify the template in `MyVuetable.vue` to look like this.
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+You can run the project now and see that the error is gone, but you won't see the pagination component just yet.
+
+This is because in order for it to work, we will need to **bind it** with Vuetable component and we'll do that in later section. Next, we will have to discuss about the pagination data structure.
+
+### Pagination data structure
+
+In order for the pagination component to work correctly, it needs some information to properly display the pagination navigation buttons and keeps track of the current position of the page.
+
+This information must be included as part of the data structure returned from the `api-url` prop and you need to tell Vuetable where it is in that data structure.
+
+The same [API endpoint](https://vuetable.ratiw.net/api/users) that we use in this tutorial already has this information. Let's have a look.
+```json
+{
+ "total": 200,
+ "per_page": 15,
+ "current_page": 1,
+ "last_page": 14,
+ "next_page_url": "https://vuetable.ratiw.net/api/users?page=2",
+ "prev_page_url": null,
+ "from": 1,
+ "to": 15,
+ "data": [
+ {...},
+ {...}
+ //...
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+The above JSON data structure is taken from [Laravel's pagination](https://laravel.com/docs/5.3/pagination#converting-results-to-json).
+
+The pagination information that Vuetable uses are
+- `total` -- total number of records available
+- `per_page` -- the number of records returned in this request/page
+- `current_page` -- the current page of this data chunck
+- `last_page` -- the last page of this data
+- `next_page_url` -- URL of the next page
+- `prev_page_url` -- URL of the previous page
+- `from` -- the start record of this page
+- `to` -- the end record of this page
+
+Without those information, Vuetable's pagination component will not work.
+
+> If you are using the API from the service provider that has different data structure or using different variable names, you will have to use [`transform()`]() hook to transform the data structure you received to the one that Vuetable can work with.
+
+### Pagination path
+
+If you run the project and happen to open the inspection console of the browser, you would notice a warning like this
+```
+vuetable: pagination-path "links.pagination" not found. It looks like the data
+returned from the server does not have pagination information or you may have
+set it incorrectly.
+```
+
+Vuetable will look for the pagination information in the returned data at the specific location and by default that location is `links.pagination`
+```json
+{
+ links: {
+ pagination: {
+ // pagination information
+ }
+ },
+ data: [
+ {...},
+ //...
+ ]
+}
+```
+
+But the data we received from the API endpoint in this tutorial, the pagination information that we need is at the root of the data structure. So, we need to tell Vuetable about this by setting the `pagination-path` prop to the root of the data structure. That is `pagination-path=""`. Now our template in `MyVuetable.vue` should look like this.
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ //...
+```
+
+### Binding pagination component
+
+Now, we are ready to bind VuetablePagination to Vuetable so that it receives pagination information that it can use. We do this in 3 steps:
+
+- listen to `vuetable:pagination-data` event on Vuetable and specify the binding handler function.
+- listen to `vuetable-pagination:change-page` event on VuetablePagination and specify the binding handler function.
+- define both of the binding handler functions in our component.
+
+#### # listen to `vuetable:pagination-data` event
+
+Vuetable emits many events during its life cycle, one of them is `vuetable:pagination-data`.
+
+> All of the event emitted by Vuetable always has `vuetable:` prefix.
+
+Whenever Vuetable received data from API endpoint, it emits `vuetable:pagination-data` event containing pagination information from the data structure.
+
+We instruct Vuetable to listen to this event using `v-on` directive. In the following code, we will use the shorthand form of `v-on` which is `@vuetable:pagination-data="onPaginationData`.
+
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ //...
+```
+
+`onPaginationData` is an event handler that we will create in the last step.
+
+#### # listen to `vuetable-pagination:change-page` event
+
+VuetablePagination emits only one event that is `vuetable-pagination:change-page`. This event will inform its parent component that the user has click on a pagination link and this should cause the loading of the given page for display.
+
+> Notice the event prefix here is `vuetable-pagination:`. If you've noticed, I'm trying to make a convention here.
+
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+
+ //...
+```
+
+
+#### # define handler function
+
+Now, let's define the handler function
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ methods: {
+ //...
+ onPaginationData (paginationData) {
+ this.$refs.pagination.setPaginationData(paginationData)
+ },
+ onChangePage (page) {
+ this.$refs.vuetable.changePage(page)
+ }
+ }
+```
+
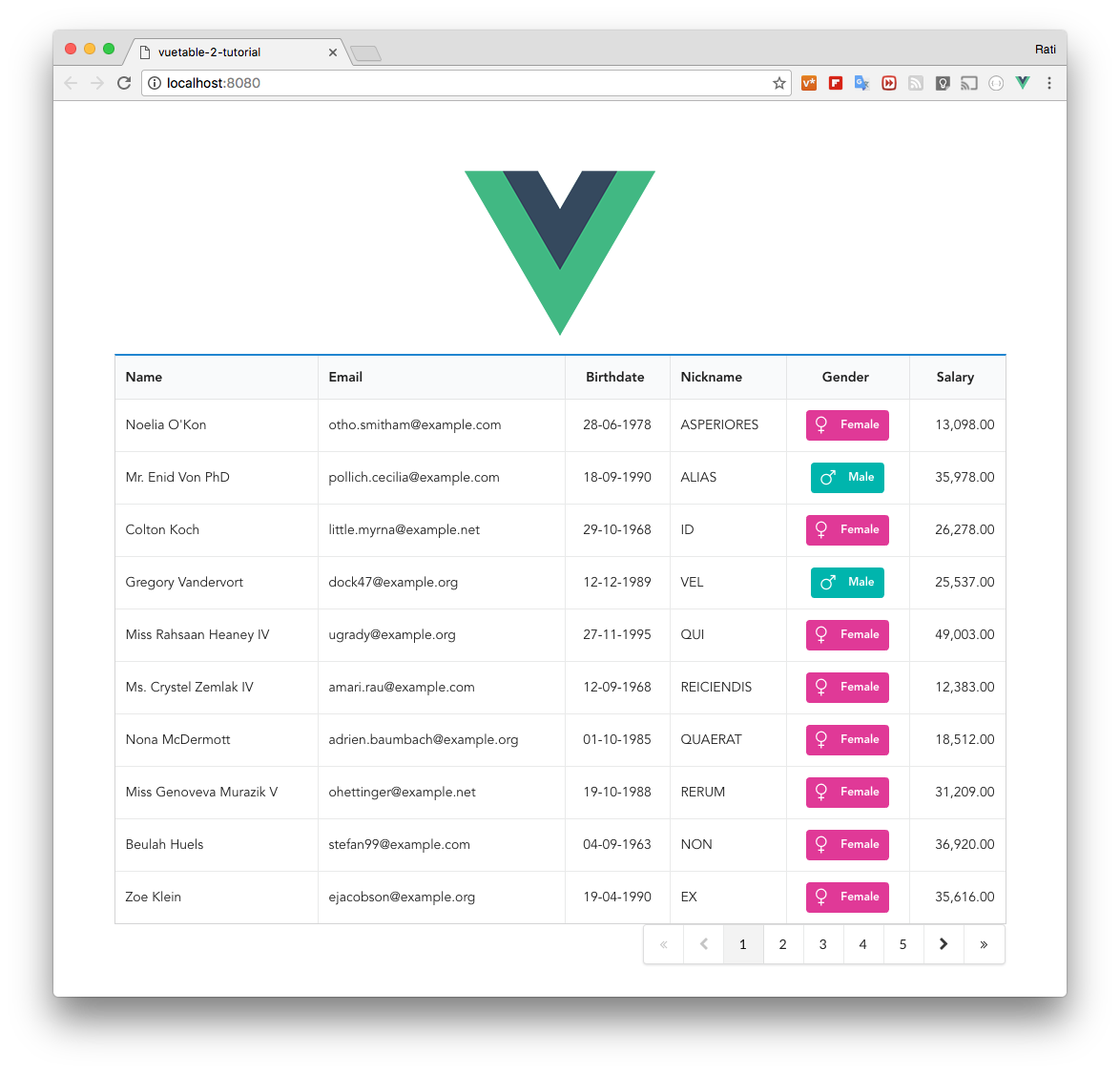
+Once you save and run it, you should now see that pagination on the page like this.
+ 
+
+> In the [first version](https://github.com/ratiw/vue-table) of Vuetable,
+> the binding of pagination component is done automatically. But in order to make it customizable, e.g. pagination component both at the top and bottom of Vuetable, we have to resort to manual binding. As you can see, this is quite easy though.
+
+Now, try changing this line:
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ import VuetablePagination from 'vuetable-2/src/components/VuetablePagination'
+```
+
+to this
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ import VuetablePagination from 'vuetable-2/src/components/VuetablePaginationDropdown'
+```
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-7)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-08.md b/docs/lesson-08.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..856b61a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-08.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+# Displaying pagination information
+
+In this lesson, we are going to add a component to display pagination information showing the number of records currently displaying and how many records are available.
+
+Vuetable also comes with pagination information component called [`VuetablePaginationInfo`](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/blob/master/src/components/VuetablePaginationInfo.vue) out of the box. We can import and bind it via `onPaginationData()` event handler.
+
+Let's see the code.
+
+```vue
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+ //...
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ //...
+
+
+
+```
+
+VuetablePaginationInfo also need to use the pagination information for display. In this case, we already have the handler for `vuetable:pagination-data` defined, so we can just add another line to `onPaginationData()`.
+
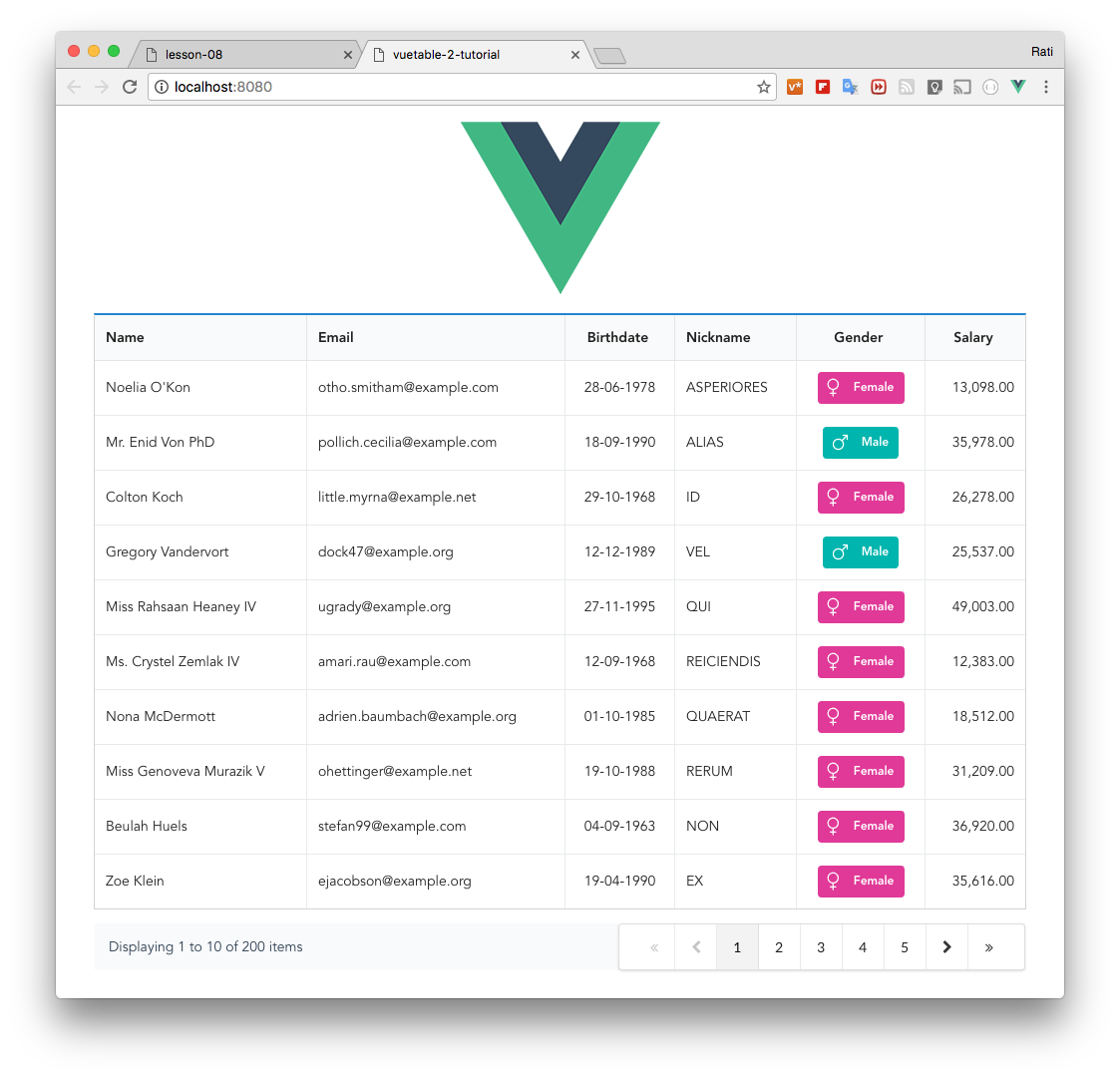
+You should notice that we are now wrapping both VuetablePagination and VuetablePaginationInfo inside another `
`, so it's easier to style it using CSS.
+
+And here's how it should look now.
+ 
+
+## Changing Information Text
+
+As you can see the default information text is something like this:
+```
+Displaying 1 to 15 of 200 items
+```
+
+You can change how the information is displayed using the following template:
+- `info-template`
+- `no-data-template`
+
+See the wiki for [VuetablePaginationInfoMixin](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/wiki/VuetablePaginationInfoMixin#-info-template)
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-8)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-09.md b/docs/lesson-09.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9dda42a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-09.md
@@ -0,0 +1,194 @@
+# Customizing Vuetable
+
+In this lesson, we will make some customizations to MyVuetable.
+
+## Displaying more records per page
+
+By default, Vuetable only request 10 records per page for displaying, but you can easily change it by specifying the number of records needed via `per-page` prop.
+
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+ //...
+
+ //...
+
+```
+
+## Adding pagination at the top
+
+Now, we are displaying 20 records per page which is quite lengthy and a bit harder to move through pages because the pagination navigation is at the bottom.
+
+Let's add another one at the top by copying the pagination that we have at the bottom, put it just before `` tag, and rename the `ref` as `paginationInfoTop` like so.
+
+```html
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+
+ //...
+
+
+
+
+
+ //...
+
+```
+
+And this new pagination component still needs to listen to `vuetable-pagination:change-page` as well, but it can just point to the existing `onChangePage()` event handler.
+
+Then, we only need to make a little change to `onPaginationData()` function.
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ onPaginationData (paginationData) {
+ this.$refs.paginationTop.setPaginationData(paginationData) // <----
+ this.$refs.paginationInfoTop.setPaginationData(paginationData) // <----
+
+ this.$refs.pagination.setPaginationData(paginationData)
+ this.$refs.paginationInfo.setPaginationData(paginationData)
+ },
+ //...
+```
+
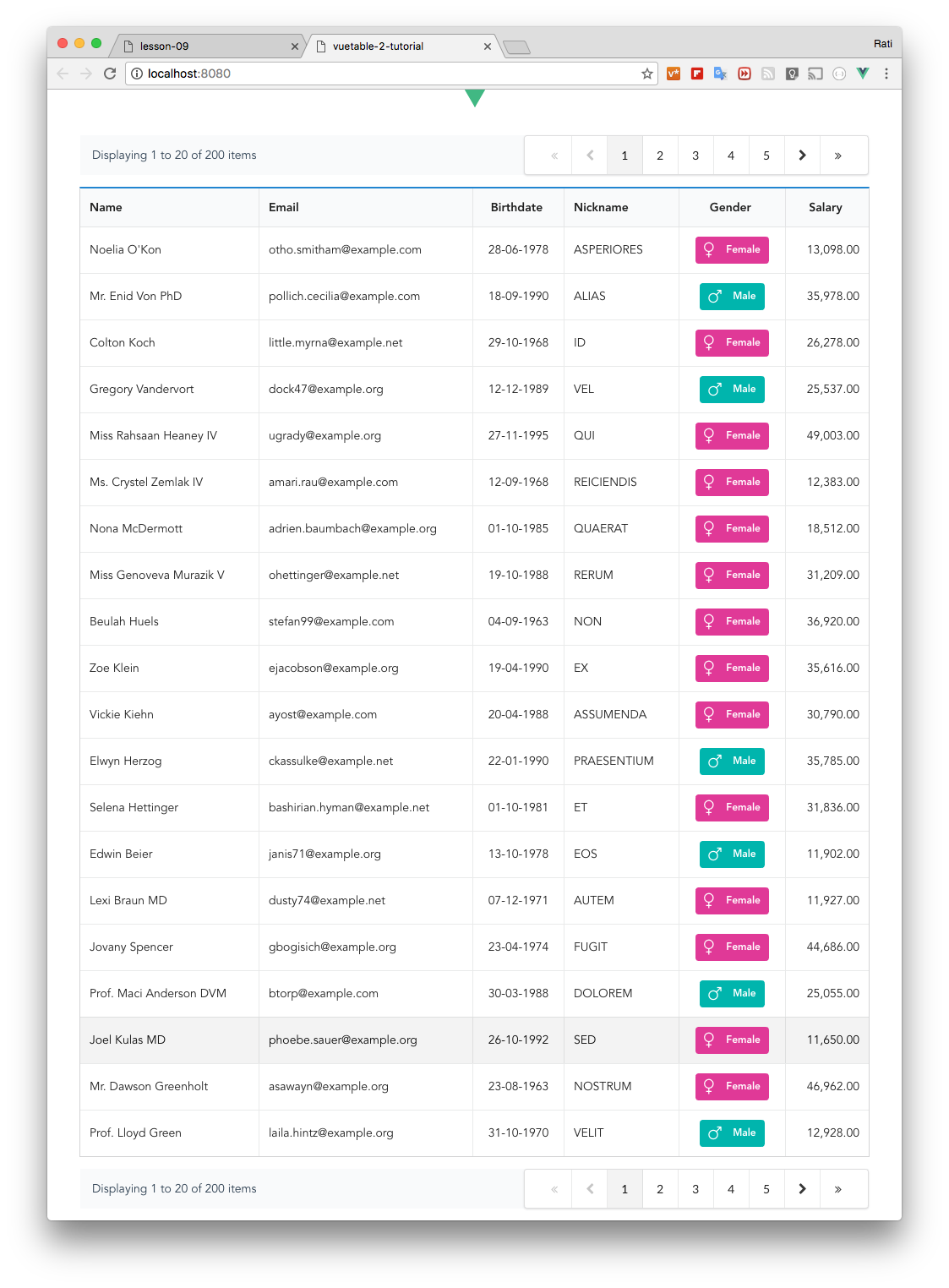
+Run the project and you should now see the pagination at the top of the table and working the same as the bottom one as well.
+
+ 
+
+## Showing/hiding columns
+
+Let's say for some reasons, you want to hide the `salary` column, how could we do that. With Vuetable, this is very easy.
+
+Remember the field definition options? There is another option called `visible` which when set to `false`, that column will be hidden.
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //...
+ {
+ name: 'salary',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'right aligned',
+ callback: 'formatNumber',
+ visible: false
+ }
+ ]
+ }
+}
+```
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-9)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-10.md b/docs/lesson-10.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..f1dbc66
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-10.md
@@ -0,0 +1,326 @@
+# Make columns sortable
+
+If your API endpoint support sorting, Vuetable can automatically interact with the API endpoint to request sorted data.
+
+## Mark field as sortable
+
+By specifying `sortField` option on the field defintion, you tell Vuetable that that particular field is sortable. Vuetable will render the column header for that field to be clickable for sorting and the ascending or descending sort icon will appear after the column name in the table header.
+
+In our tutorial project, we would like to make all fields sortable, so we have the add `sortField` option for every field and we have to turn the `name` and `email` field from simple string to field definition object as well.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ //...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ {
+ name: 'name',
+ sortField: 'name'
+ },
+ {
+ name: 'email',
+ sortField: 'email'
+ },
+ {
+ name: 'birthdate',
+ sortField: 'birthdate',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'center aligned',
+ callback: 'formatDate|DD-MM-YYYY'
+ },
+ {
+ name: 'nickname',
+ sortField: 'nickname',
+ callback: 'allcap'
+ },
+ {
+ name: 'gender',
+ sortField: 'gender',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'center aligned',
+ callback: 'genderLabel'
+ },
+ {
+ name: 'salary',
+ sortField: 'salary',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'right aligned',
+ callback: 'formatNumber'
+ }
+ ]
+ }
+ },
+ //...
+```
+
+Run the project and try it. Now, all columns are sortable!
+
+You can mark as many field as sortable as you want provided that your API endpoint support sorting for those fields. If your API does not support sorting for any of the field you specified, your users will not get the result they expected.
+
+You may notice that the `sortField` usually is the `name` of the field. But it doesn't have to be.
+
+Sometimes, the `name` of the field is just an alias of a computed column in the SQL's `select` command. Let's add the `age` field in MyVuetable, just before the `birthdate` field and also make it sortable.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ // ...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //...
+ {
+ name: 'age',
+ sortField: 'age',
+ dataClass: 'center aligned'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+If you run the project and click on "Age" column, you'll see that it doesn't get the sort correctly. Also, if you check the browser console, you will also see the 505 error returning from the server as well.
+
+This is because the `age` field is a computed column. It does not have a real column in the database table, so the SQL cannot find the column named `age` to do the `ORDER BY` command on. So, it throws the error back.
+
+The `age` field is actually computed its value from `birthdate` field, so we can specify the `birthdate` as the `sortField` option instead and the result will still be correct.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ // ...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ //...
+ {
+ name: 'age',
+ sortField: 'birthdate', // <----
+ dataClass: 'center aligned'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+
+
+## Multi-column sorting
+
+By default, Vuetable will only work in single column sorting mode. But if you need to do multi-column sorting, you can set `multi-sort` prop to `true`. Then, you can use the `Alt` key (for Windows) or `Opt` key (for Mac) to select subsequent column for sorting. Clicking on the same column will cycle the sort direction from ascending to descending and again to unselect for sorting.
+
+```html
+
+
+
+```
+
+If you would like to change the `Alt` key to something else, you can use `multi-sort-key` prop to specify one of the following value:
+
+- `alt` (default) -- Alt / Option key
+- `ctrl` -- Ctrl / Control key
+- `meta` -- Window / Command key
+- `shift` -- Shift key
+
+```html
+
+
+
+```
+
+Again, if you API does not support multi-column sorting, the displaying results will not be as expected.
+
+## Changing ascending/descending icon
+
+Ascending/descending icon are just CSS classes wrap inside `` tag and you can change it to any icon you like if your CSS framework support it.
+
+Here is an example on changing it to use Bootstrap 3 CSS, set the `ascending-icon` and `descending-icon` in the `css` prop appropriately.
+
+```vue
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+For more information, see [`css`](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/wiki/Vuetable-Properties#-css) property of Vuetable.
+
+## Setting default sort order
+
+You can use `sort-order` prop to specify the initial sort order. For example, you would like the data to be initially sorted by `email` field, you can do so by:
+
+```vue
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+
+## Play with it
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-10)
diff --git a/docs/lesson-11.md b/docs/lesson-11.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..49e69d6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-11.md
@@ -0,0 +1,442 @@
+# Using special fields
+
+Special fields are predefined field for specific purpose and their names are always started with double underscore characters `__`.
+
+There are 5 special fields currently defined in Vuetable.
+
+- [`__sequence`](#__sequence)
+- [`__handle`](#__handle)
+- [`__checkbox`](#__checkbox)
+- [`__component`](#__componentname)
+- [`__slot`](#__slotname--v120)
+
+To use any of these special fields, you just define another field in the `fields` prop and use the special field as the name of the field.
+
+### __sequence
+
+If you would like to display the sequence number of the records based on the pagination information, you can do that using `__sequence` special field.
+
+Let's add the sequence number to MyVuetable.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ // ...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ {
+ name: '__sequence', // <----
+ title: '#',
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'right aligned'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+```
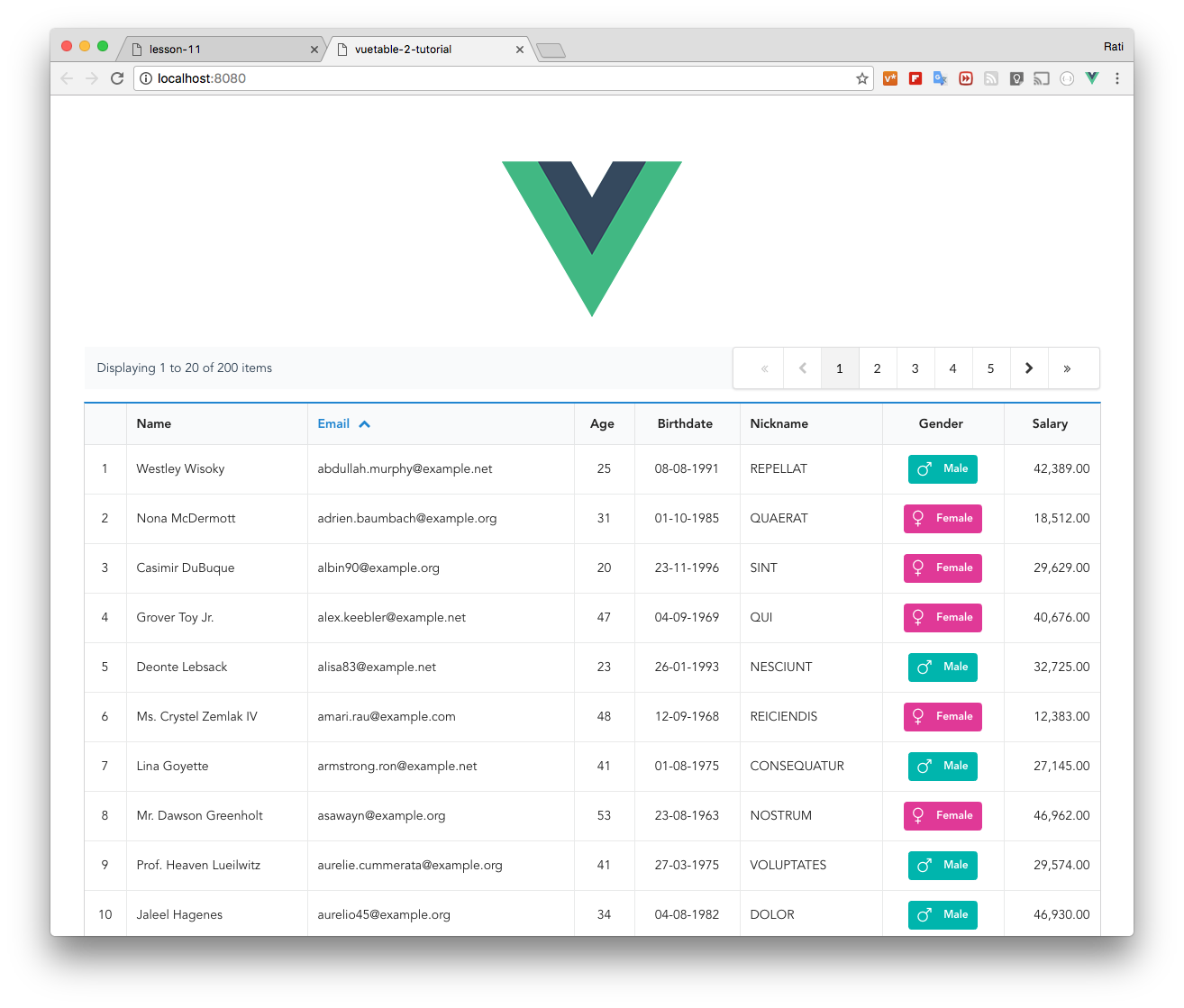
+
+You should now see the sequence column appears on the left side of the table.
+
+
+
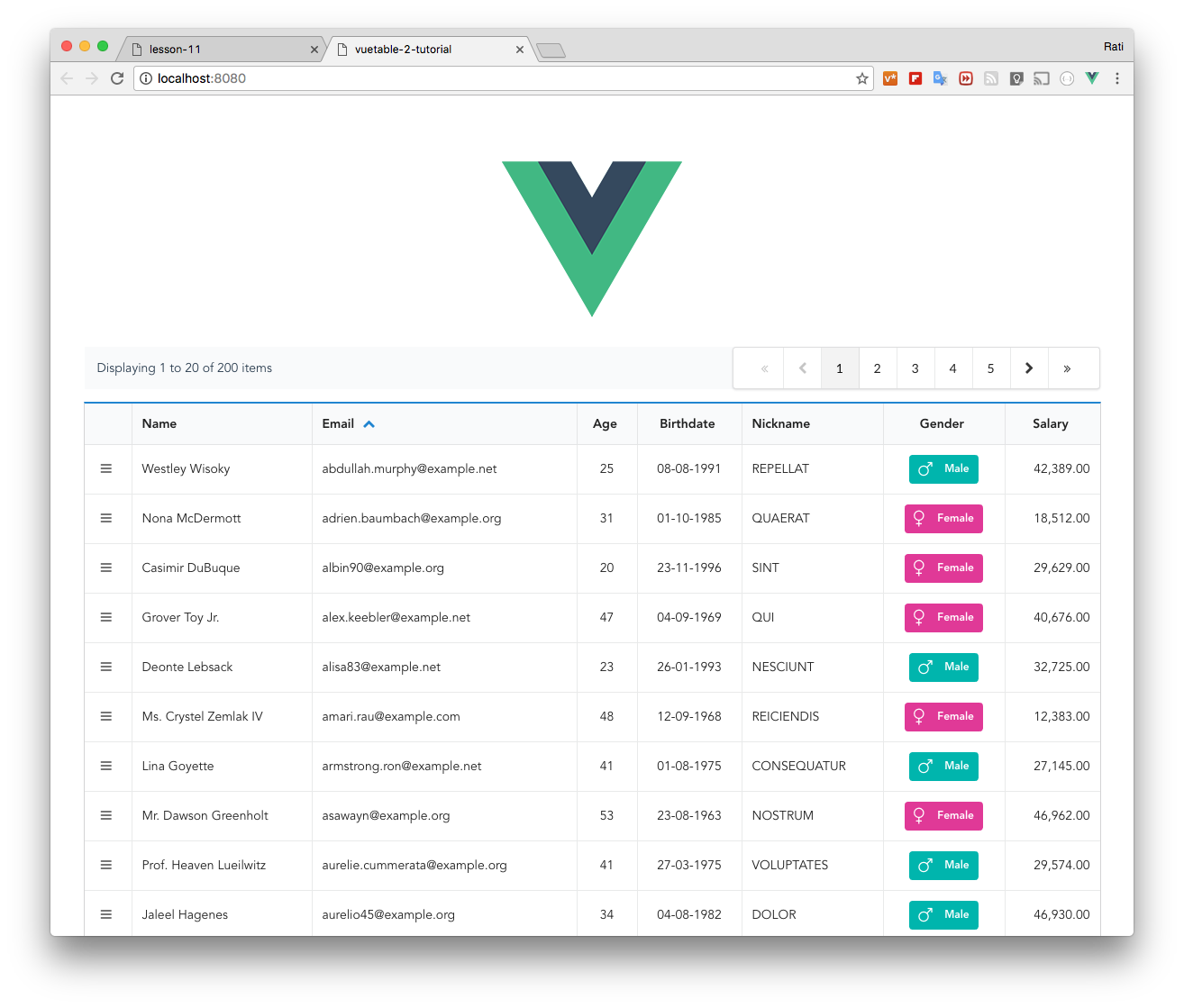
+### __handle
+
+This one was created specifically because we need to make a handle icon for [Sortable.js](https://github.com/rubaxa/Sortable).
+
+You can use `css.sortHandleIcon` to change the icon that suit your task.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ // ...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ {
+ name: '__handle', // <----
+ dataClass: 'center aligned'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+
+
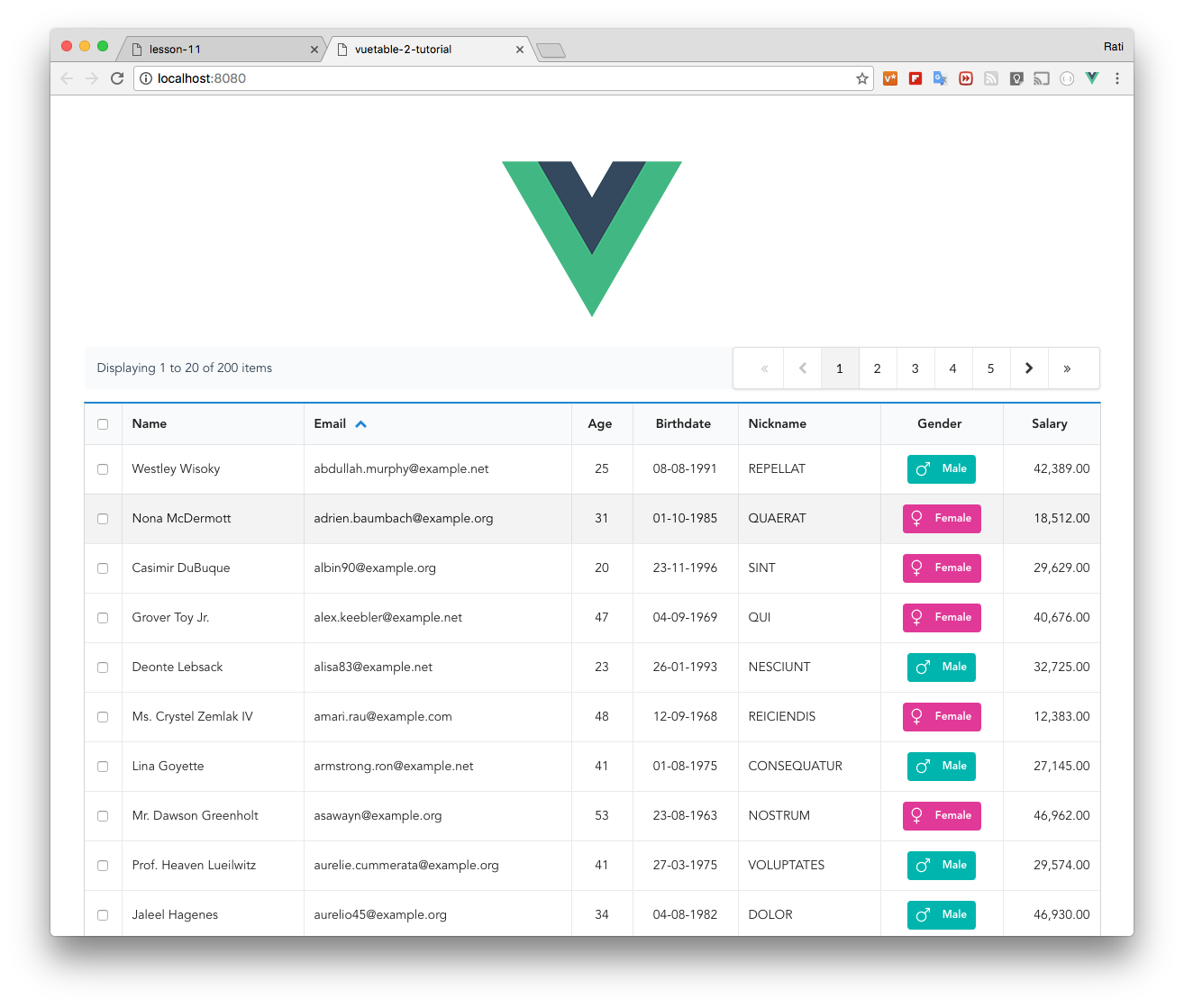
+### __checkbox
+
+The `__checkbox` special field will display checkbox column for each row and also on the header row to allow select/unselect all functionality.
+
+In order for Vuetable to keep track of the checkbox state of each data row.
+By default, `__checkbox` will use `id` field for that purpose as it usually unique for each row. That also means your data will have to have `id` column.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ // ...
+ data () {
+ return {
+ fields: [
+ {
+ name: '__checkbox', // <----
+ titleClass: 'center aligned',
+ dataClass: 'center aligned'
+ },
+ //...
+ ]
+ }
+ }
+```
+
+Run the project and try it out!
+
+
+
+If you do not have `id` in your data structure, or want to use another field that could also uniquely identify each column, you have to specify that using `track-by` prop.
+
+For example, if you want to use `item_code` field instead, you can do so like this.
+
+```javascript
+ // MyVuetable.vue
+
+ // ...
+
+ //...
+```
+
+You can see what rows are selected by looking into [`selectedTo`](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2/wiki/Vuetable-Data#-selectedto) property of Vuetable.
+
+### __component:<name>
+
+The `__component` special field allows you to create a component to handle the row data the way you want.
+
+In this tutorial, we will create a `custom-actions` component to display buttons that will allow the user to interact with the row data.
+
+Add a new file to your project, let's called `CustomActions.vue`. Here's the code.
+```vue
+ // CustomActions.vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+> Please note that we are also make use of `
+```
+
+Now, run the project and everything should still work exactly the same. The only difference is that we are now passing relevant properties from our `App` component down to our `MyVuetable` component. This should make it much more reusable.
+
+However, there is one more thing that we still haven't look into which is the [scoped slots](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#Scoped-Slots) for our `actions` buttons which is still embedded inside our `MyVuetable`.
+
+The scoped slots cannot be passed down like any other properties. We will deal with this in the next lesson.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/docs/lesson-17.md b/docs/lesson-17.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..db70579
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-17.md
@@ -0,0 +1,368 @@
+# Passing Scoped Slot to MyVuetable
+
+In the last lesson, we have successfully create properties in our `MyVuetable` component allowing passing data in from the main component/instant. But the only remaining thing we are not able to do is the [scoped slots](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#Scoped-Slots).
+
+Scoped slots has been newly introduced in Vue 2.1 and it is a very powerful concept when working with Vue.js. It offers a more convenient way of flexible content distribution. Before the introduction of scope slots, you would have to create another component for the job.
+
+## The Problem
+
+As of the current release of Vue 2.3, there is still no way to pass the scoped slot down into the component via template. The only way possible is to implement the `render` function where you'll have access to `scopedSlots` data object. This will allow you to pass down the scoped slot into your component. But this means you will have to give up the template and render your component using the `render` function only.
+
+This seems like a daunting task. Luckily, in our case, this is not that hard but you will need some background knowledge before proceeding. Read the following topic in Vue documentation first, then come back to continue with the tutorial. You don't need to understand everything though.
+- [Scope slots](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#Scoped-Slots)
+- [Render function](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html)
+
+
+## Converting `` to render function
+
+It is possible to start making your component with `render` function from the beginning if your component is not so complex (e.g. does not have a complex html structure). But template is actually more natural and a lot easier to comprehend, especially if you're still new to making Vue component.
+
+In fact, you don't really have to care or learn about `render` function until you really need to use it. Since we would like our users to be able to use scoped slots from our `MyVuetable` component and pass this down to Vuetable, we need to
+be able to access to `scopedSlots` data object which only available inside the `render` function.
+
+### Reviewing the ``
+
+So, let's begin by reviewing the current template of our `MyVuetable`. This will help guide us on what we need to do.
+
+```vue
+
+
+
+
+ //... this used to be where scoped slot "actions" was ...
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+> Please note that the template above does not include the scoped slots "actions".
+> As it should be passed down from the parent component, so it no longer needs to be there.
+
+### **Looks quite intimidating, isn't it?**
+
+__Fear Not!__ It's easier than you might think. There's a trick to that and we'll show you how.
+
+### Digesting the Template
+
+The `render` function is nothing more than mimicking the browser in rendering the HTML. So, if you look at the stardard HTML page, you would see layers of layers of HTML tags inside with the outermost layer is the `` tag.
+
+```html
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ //...
+
+
+ //...
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+The `render` function that you're going to write is exactly the same. You render from the outermost layer into the innermost one, step by step, passing the [`createElement` argument](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#createElement-Arguments) (usually denoted with `h` for brevity) down to the inner layer, so that it can be used to render other stuff inside its block.
+
+Let's digest our template down a bit and I'll explain why it is digestible to this.
+
+```vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+### Look much better, isn't it?
+
+After all, our component structure wasn't so complex. What makes it complex is the functionality inside that has been exposed through its properties and events. When we strip them down, what's left is the skeleton that we can comprehend.
+
+That, however, doesn't mean that we do not need those attributes and directives we omit. We do, but we will deal with them one by one inside its own block.
+
+Let's discuss each block and starting writing our `render` function.
+
+## The "container" `
` block
+
+Every Vue component must has exactly one root element, which in our case is the outermost `
` block. To be precise, the actual block looks like this. (We will leave out the `` tag from now on.)
+
+```html
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+- It has `ui` and `container` classes
+- It contains __three__ children, which are
+ - ``
+ - ``, and
+ - pagination `
`
+
+With this information, we can start writing our `render` function for the outermost layer. And here's what the `render` function looks like.
+
+```javascript
+ render (h) {
+ return h(
+ 'div', //.. first parameter,
+ {}, //.. second parameter,
+ [] //.. third parameter
+ )
+ },
+```
+
+> __Note__
+> The `render` function is not inside the `methods` section, it lives at the same level as the `props`, `data`, and `methods` section!
+
+When you declare the `render` function, Vue will pass in the `createElement` argument as a parameter. Since we are going to use this argument very often, we should name it very short. And by convention, it usually names `h`.
+
+The `createElement` argument (from now on will be referred to as `h`) is actually a function, so to use it you have to call it and supplies parameters to it and must return itself back to its parent so that the execution can be chained and handled properly by the main instance.
+
+- The first parameter is the "tag" that you want to render out as HTML tag, in this case, a `div`.
+- The second parameter _(optional)_ is the [Data Object](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#The-Data-Object-In-Depth) describing the characteristics of the element to be rendered.
+- The third parameter _(optional)_ can be either a string that will be inside the element tag (e.g. `Hello`) _or_ an array of its children.
+
+> __Note__
+> In this tutorial, we will always write its parameters in its own line, so that it is easier to notice.
+
+Here is the complete `render` function of our outermost `div` block.
+
+```javascript
+ render (h) {
+ return h(
+ 'div',
+ {
+ class: { ui: true, container: true }
+ },
+ [
+ h('filter-bar'),
+ this.renderVuetable(h),
+ this.renderPagination(h)
+ ]
+ )
+ },
+```
+
+We specify that this `div` should have `ui` and `container` class inside the [Data Object](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#The-Data-Object-In-Depth) in the second parameter.
+
+In the third parameter, we specify that this `div` block will contain __3__ children:
+- the first one (`filter-bar`) does not have any attribute, so we just use `h` to render it out.
+- the second one (`vuetable`) will contain quite a lot information, so we just delegate it to another method (`renderVuetable`) to do the rendering of its block and pass in the `h` for its use inside.
+- the third one will also contain some attributes, so we will also delegate to another method (`renderPagination`) to render its own block as well.
+
+Looks how we build the `render` function to follow our digested template.
+
+## The `` block
+
+Now, let's look at the `` block and how the `renderVuetable` method will look like. Again, we should start by looking at the template of the `` block.
+
+```html
+
+```
+
+And here is `renderVuetable` function that we've converted from the template above.
+
+```javascript
+ methods: {
+ renderVuetable(h) {
+ return h(
+ 'vuetable',
+ {
+ ref: 'vuetable',
+ props: {
+ apiUrl: this.apiUrl,
+ fields: this.fields,
+ paginationPath: "",
+ perPage: 10,
+ multiSort: true,
+ sortOrder: this.sortOrder,
+ appendParams: this.appendParams,
+ detailRowComponent: this.detailRowComponent,
+ },
+ on: {
+ 'vuetable:cell-clicked': this.onCellClicked,
+ 'vuetable:pagination-data': this.onPaginationData,
+ },
+ scopedSlots: this.$vnode.data.scopedSlots
+ }
+ )
+ },
+ //...
+```
+The structure looks the same as in the main `render` function for the `div` block we did earlier. The main different is the Data Object describing this element contains so much more information. Let's break it down:
+
+- The first parameter, we specify that we want to render `vuetable` tag
+- The second parameter, the Data Object (you may need to re-read [this](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#The-Data-Object-In-Depth) again). If you trace back to the template, you should clearly see how it is converted to each key in the Data Object.
+- The third parameter, the children of this element. In this case, we expect to have the `scopedSlots` pass down from the parent and refer to those scoped slots via `$vnode.data.scopedSlots`.
+
+Now that we've seen the most complex block, the next one should be relatively easy.
+
+## The "pagination" `
` block
+
+Here is the template for the pagination block.
+
+```html
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+And here is the render function for this block, `renderPagination`.
+
+```javascript
+ methods: {
+ //..
+ renderPagination(h) {
+ return h(
+ 'div',
+ { class: {'vuetable-pagination': true, 'ui': true, 'basic': true, 'segment': true, 'grid': true} },
+ [
+ h('vuetable-pagination-info', { ref: 'paginationInfo' }),
+ h('vuetable-pagination', {
+ ref: 'pagination',
+ on: {
+ 'vuetable-pagination:change-page': this.onChangePage
+ }
+ })
+ ]
+ )
+ },
+ //...
+```
+
+The interesting one is the third parameter where we supply an array of its children.
+
+In this case, each child is quite simple and does not have any children of its own, so we use `h` to render it in-place. No need to create another function for each of them.
+
+## There, you have it!
+
+We have now completed converting the template to `render` function. So, you can now delete the whole `` section from `MyVuetable.vue` file.
+
+__But our task is not finish yet.__
+
+Remember, we have left out the "actions" scoped slot from the template at the begining? Now, we need to move it into the `App.vue`. And as it needs to call `onAction` method, we also need to move `onAction` into `App.vue` as well.
+
+And here is how the `App.vue` should look.
+```vue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+[Source code for this lesson](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-2-tutorial/tree/lesson-17)
+
diff --git a/docs/lesson-18.md b/docs/lesson-18.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..3845498
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/lesson-18.md
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+# Using Twitter's Bootstrap CSS with Vuetable
+
+## index.html
+- Replace Semantic UI CSS and JS
+
+## Changes related to Vuetable, VuetablePagination, and VuetablePaginationInfo
+- create a new file to store CSS for those components
+- field def
+- use `css` prop of each component to assign appropriate config object
+- buttons and icons in "actions" scoped slot
+
+## Changes outside of Vuetable
+- filter-bar
+- app CSS
+-
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/prerequisite.md b/docs/prerequisite.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..d126166
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/prerequisite.md
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+# Before We Begin
+We need to do the following first
+- Install the required tools
+- sample API endpoint
+
+## Install the required tools
+
+> If you've already install `node`, `yarn` and `vue-cli`, you can skip to the next section. Nothing more fancy here!
+
+If you haven't already known, we need Node.js, yarn, and vue-cli to compile and run our Vue.js project. So, click the link below to visit the corresponding websites to install them in your development environment.
+
+ - [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/)
+ - [Yarn](https://yarnpkg.com/) -- _if you prefer a slower workflow, you can also use `npm`_.
+ - [vue-cli](https://github.com/vuejs/vue-cli)
+
+
+## Create a tutorial project with Vue CLI
+
+### Create a new project using vue-cli
+
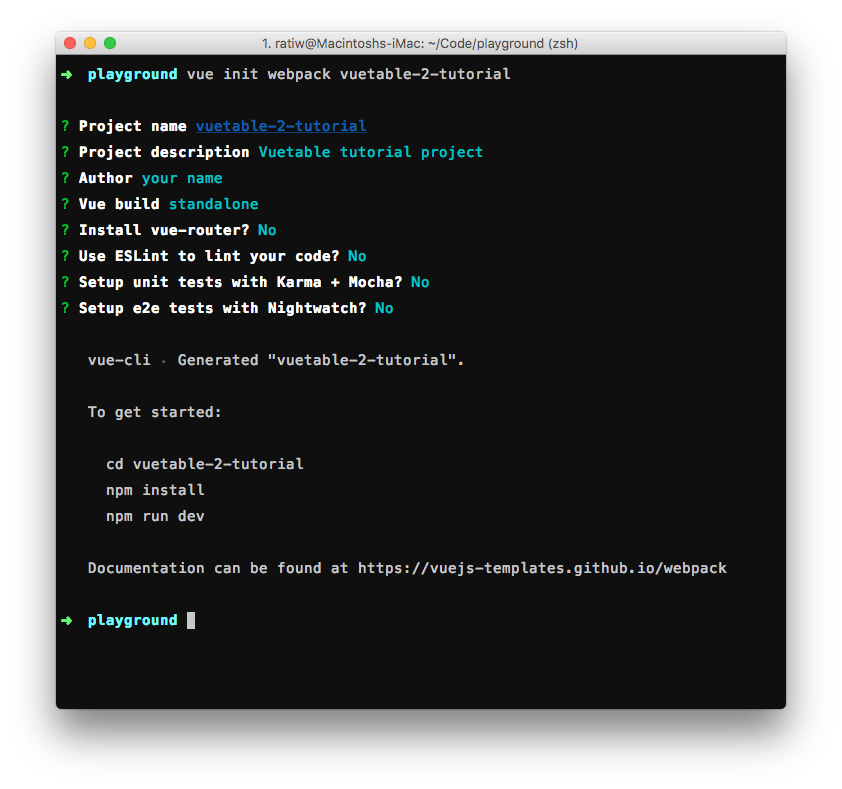
+Vue-cli is an excellent tool to help scaffold Vue.js project. We will use it to create our tutorial project as well. Just type or copy this to your command line.
+```shell
+ $ vue init webpack vuetable-2-tutorial
+```
+
+Once you press Enter, vue-cli will download the [webpack template](https://github.com/vuejs-templates/webpack) and start asking some questions to setup the project for us.
+
+- `Project name`
+ Enter the project name you like or just accept the default by pressing Enter.
+
+- `Project description
+ Enter project description or pressing Enter to accept the default.
+
+- `Author`
+ Enter your name as the author of the project.
+
+- `Vue build`
+ Select which build of Vue.js you would like to use in this project. In this case, we'll select the first option which is a "standalone" version (Runtime + Compiler). Please see the difference between these versions [here](https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/installation.html#Standalone-vs-Runtime-only-Build).
+
+- `Install vue-router? (Y/n)
+ Press `N` to answer `No` here as we do not need to use vue-router in our tutorial.
+
+- `Use ESLint to lint your code?`
+ Please select `No` for this option as it gives you less headache to start with. If you want to keep your mind busy or want to learn more about it, go read it [here](http://eslint.org/).
+
+- `Setup unit tests with Karma + Mocha?`
+ Just select `No` for the moment. We won't need to test anything in our tutorial. But when the time comes, just answer `Yes` and be grateful to the tool's author that make your life a lot easier.
+
+- `Setup e2e tests with Nightwatch?`
+ Just select `No` for the same reason as above.
+
+Here is the example.
+
+ > Project name: **_vuetable-2-tutorial_**
+ > Project description: **_Vuetable tutorial project_**
+ > Author: **_your name_**
+ > Vue build: **_standalone (Runtime + Compiler)_**
+ > Install vue-router? **_No_**
+ > Use ESLint to lint your code? **_No_**
+ > Setup unit tests with Karma + Mocha? **_No_**
+ > Setup e2e tests with Nightwatch? **_No_**
+
+ 
+
+Once the installation is done, you have to `cd` into the project directory to install all the dependcies of the project.
+
+```shell
+ $ cd vuetable-2-tutorial
+ $ yarn install
+```
+
+This might take awhile as `yarn` trying to install and link all the depencies specify in the `package.json` for you. Once it is finished, you can run the project like this.
+
+```shell
+ $ yarn run dev
+```
+
+You should now see the project running in the web browser like this.
+ 
+
+The project is now running in watch mode with Hot Reload. Which means you can continue to edit the source code and once you save it, the browser will automatically be upadted to reflect the changes you've made.
+
+For now, close the page and type `Ctrl+C` in the command line to exit the watch mode.
+
+## Sample API endpoint
+
+Vuetable is designed to be a **presentation layer** of the data on the client side, so it needs to work with API endpoint. For the purpose of this tutorial and the example projects, we alredy have set up an API endpoint for it.
+
+Currently, the API endpoint is at https://vuetable.ratiw.net/api/users
+
+> If you are interested, the source code of the project is located [here](https://github.com/ratiw/vuetable-sample-api-endpoint)
+
+Basically, this API endpoint returns a collection of fake users and it supports the following features:
+
+- Pagination (`page`)
+ You can specify which "page" of data you're interested by using `page` in the query string.
+
+ page=
+
+ The returned data will also contain pagination information. See [JSON result](http://vuetable.ratiw.net/api/users) from the sample API endpoint.
+
+- Result limit (`per_page`)
+ You can specify how many records you would like for a page by using `per_page in the query string.
+
+ per_page=
+
+- Sorting (`sort`)
+ You can request the sorted result from the API endpoint using `sort` in the query string.
+
+ sort=|
+
+ All of the columns directly in the User are sortable, but not those that are in the embedded data like `group` and `address`.
+
+ > If you would like your API to support sorting in the embedded data, you'll have to use SQL's `JOIN` to expose it.
+
+- filtering (`filter`)
+ You can request the filtered result from the API endpoint using `filter` in the query string.
+
+ filter=
+
+ The `` is a string to be searched for in `name`, `nickname`, and `email` fields.
+
+The values for `page`, `per_page`, `sort`, and `filter` in the query string will be populated automatically by Vuetable before sending the request to the server.
+
+If you would like to use other terms or the API you're working with use different terms, you can use `query-params` prop change them accordingly and Vuetable will use those terms instead.