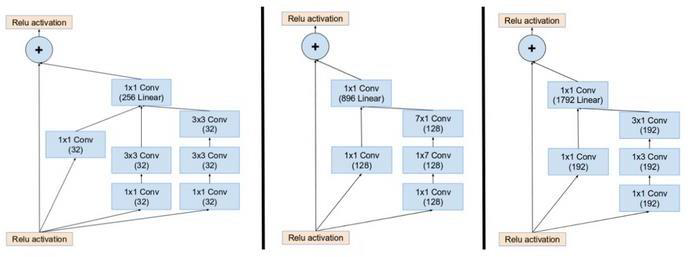
The Inception-ResNet like the Inception v4 uses the same two reduction blocks. But uses inception-resnet blocks instead. This is done so that the output of the inception module is added to the input. Each of these inception-resnet blocks consist of a shortcut connection. This greatly reduces the effect of vanishing gradient problem, i.e. helps the model to memorize the patterns easier no matter how deep the neural network is. The network becomes selective of the patterns it wants to learn. Reduction blocks control the breadth and depth of the network by providing max pooling and convolutional filters.
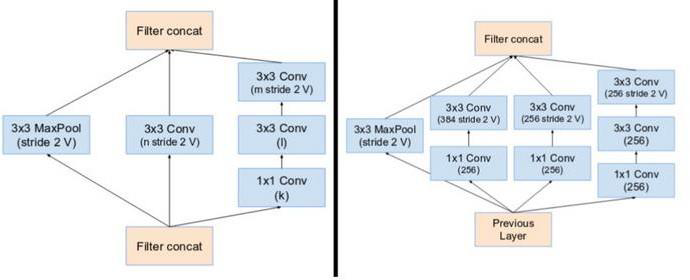
Reduction block A has
- a 3x3 MaxPool filter,
- a 3x3 convolutional filter,
- a 1x1 convolutional filter followed by 2 3x3 convolutional filters.
Reduction block B has
- a 3x3 MaxPool filter
- a 1x1 convolutional layer followed by a 3x3 convolutional layer.
- a 1x1 convolutional layer followed by a 3x3 convolutional layer with different number of channels in output.
- a 1x1 convolutional layer followed by 2 3x3 convolutional layers one over another.
Figure 1. Inception-ResNet modules: A, B, and C
Figure 2. Reduction Blocks A and B
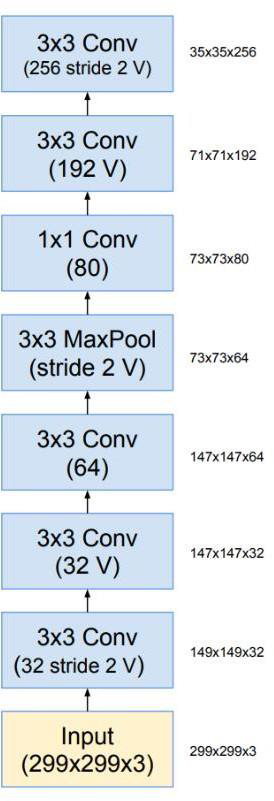
Figure 3. Pre-processing Unit (Stem)
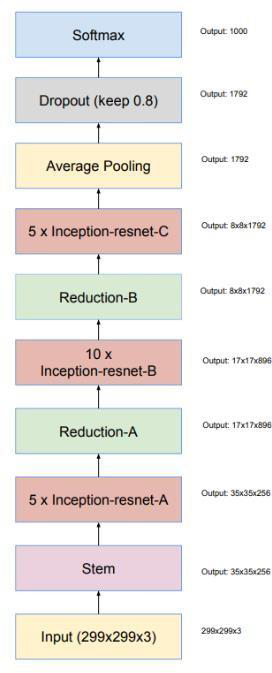
Figure 4. Overall model
Adversarial attacks deceive the model into giving away sensitive information, making incorrect predictions, or corrupting them. Decisions taken by networks in classification can be manipulated by adding carefully crafted noise to an image which we often refer to as an ‘adversarial attack’ on a neural network. If done well this noise is barely perceptible and can fool the classifier into looking at a certain object and thinking that it is a totally different object. We have used untargeted attacks to corrupt the images, i.e., the goal is simply to make the target model misclassify by predicting the adversarial example as a class other than the original class.
Experimental results on MNIST, CIFAR-10, and ImageNet show that Elastic-net Attack to Deep neural networks (EAD) yields a distinct set of adversarial examples. More importantly, EAD leads to improved attack transferability suggesting novel insights on leveraging L1 distortion in generating robust adversarial examples.
ElasticNet Attack - https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.04114
Retinal OCT Images (optical coherence tomography)
InceptionResnetV1 Pytorch (Config 1).ipynb - All the layers in the model are trainable.
InceptionResnetV1 Pytorch (Config 2).ipynb - The first 9 layers in the model are freezed.
- Nithil Eshwar Mani
- Chiranjeevi
- Abiramashree
From Department of Computer Science & Engineering, College of Engineering, Guindy, Anna University