Methurator is a Python package designed to estimate CpGs saturation for DNA methylation sequencing data.
- 1. Dependencies and Notes
- 2. Installation
- 3. Quick Start
- 4. Command Reference
- 5. Example Workflow
- 6. How do we compute the sequencing saturation?
- methurator uses SAMtools and MethylDackel internally for BAM subsampling, thus they need to be installed.
- When
--genomeis provided, the corresponding FASTA file will be automatically fetched and cached. - Temporary intermediate files are deleted by default unless
--keep-temporary-filesis specified.
You can install methurator in several ways:
pip install methuratorconda create -n methurator_env conda::methurator
conda activate methurator_envdocker pull quay.io/biocontainers/methurator:2.1.1--pyhdfd78af_0
docker run quay.io/biocontainers/methurator:2.1.1--pyhdfd78af_0 methurator -hThe gt-estimator command estimates CpGs sequencing saturation at higher depth than the observed one. This is the recommended approach for extrapolation analysis.
methurator gt-estimator --fasta tests/data/genome.fa tests/data/Ecoli.csorted.bamThis command generates:
- Summary YAML file (
methurator_summary.yml) — Contains metadata, model parameters, and extrapolation results with:- Extrapolation factor (t) values from 0 to
--t-max(default: 10.0) - Boolean indicating interpolated (t ≤ 1) vs extrapolated (t > 1) data
- Total CpGs predicted at each t value
- Theoretical asymptote (maximum CpGs, computed at t = 1000)
- Number of reads observed at full sequencing depth (t = 1)
- Confidence intervals (if
--compute_ciis enabled)
- Extrapolation factor (t) values from 0 to
The downsample command performs BAM downsampling according to specified percentages and coverage levels:
methurator downsample --fasta tests/data/genome.fa tests/data/Ecoli.csorted.bamThis command generates:
- CpG summary — number of unique CpGs detected in each downsampled BAM
- Reads summary — number of reads in each downsampled BAM
- Summary YAML — consolidated file with all data and run metadata
Use the plot command to visualize the results, including the asymptote line and the number of reads at each t:
methurator plot --summary output/methurator_summary.yml| Argument | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
BAM (positional) |
Path to a single .bam file or to multiple ones (e.g. files/*.bam). |
— |
--outdir, -o |
Output directory. | ./output |
--fasta |
Path to the reference genome FASTA file. If not provided, it will be automatically downloaded based on --genome. |
— |
--genome |
Genome used for alignment. Available: hg19, hg38, GRCh37, GRCh38, mm10, mm39. |
— |
--minimum-coverage, -mc |
Minimum CpG coverage to consider. Can be a single integer or a list (e.g. 1,3,5). |
1 |
--t-step |
Step size for extrapolation factor (t) predictions. | 0.05 |
--t-max |
Maximum extrapolation factor (t) value. | 10.0 |
--compute_ci |
Compute confidence intervals using bootstrap replicates. | False |
--bootstrap-replicates, -b |
Number of bootstrap replicates for CI computation. | 30 |
--conf |
Confidence level for bootstrap intervals. | 0.95 |
--mu |
Initial mu parameter for negative binomial distribution in EM algorithm. | 0.5 |
--size |
Initial size parameter for negative binomial distribution in EM algorithm. | 1.0 |
--mt |
Constraint for rational function approximations. | 20 |
--rrbs |
If set to True, MethylDackel will use the RRBS flag (--keepDupes). | False |
--threads, -@ |
Number of threads to use. | Available threads - 2 |
--keep-temporary-files, -k |
Keep temporary files after analysis. | False |
--verbose |
Enable verbose logging. | False |
--help , -h |
Print the help message and exit. | |
--version |
Print the package version. |
| Option | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
BAM (positional) |
Path to a single .bam file or to multiple ones (e.g. files/*.bam). |
— |
--outdir, -o |
Output directory. | ./output |
--fasta |
Path to the reference genome FASTA file. If not provided, it will be automatically downloaded based on --genome. |
— |
--genome |
Genome used for alignment. Available options: hg19, hg38, GRCh37, GRCh38, mm10, mm39. |
— |
--downsampling-percentages, -ds |
Comma-separated list of downsampling percentages between 0 and 1 (exclusive). | 0.1,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8 |
--minimum-coverage, -mc |
Minimum CpG coverage to consider for saturation. Can be a single integer or a list (e.g. 1,3,5). |
3 |
--rrbs |
If set, MethylDackel extract will consider the RRBS nature of the data by adding the --keepDupes flag. |
False |
--threads, -@ |
Number of threads to use during downsampling. | All available threads |
--keep-temporary-files |
If set, temporary files will be kept after analysis. | False |
--verbose |
Enable verbose logging. | False |
--help, -h |
Print the help message and exit. | — |
--version |
Print the package version. | — |
| Argument | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
--summary, -s |
Path to the YML summary file. | |
--outdir, -o |
Output directory. | ./output |
--verbose |
Enable verbose logging. | False |
--help , -h |
Print the help message and exit. | |
--version |
Print the package version. |
# Run Chao estimator on BAM file
methurator gt-estimator --genome hg19 my_sample.bam --config_ci
# Generate plots from the results
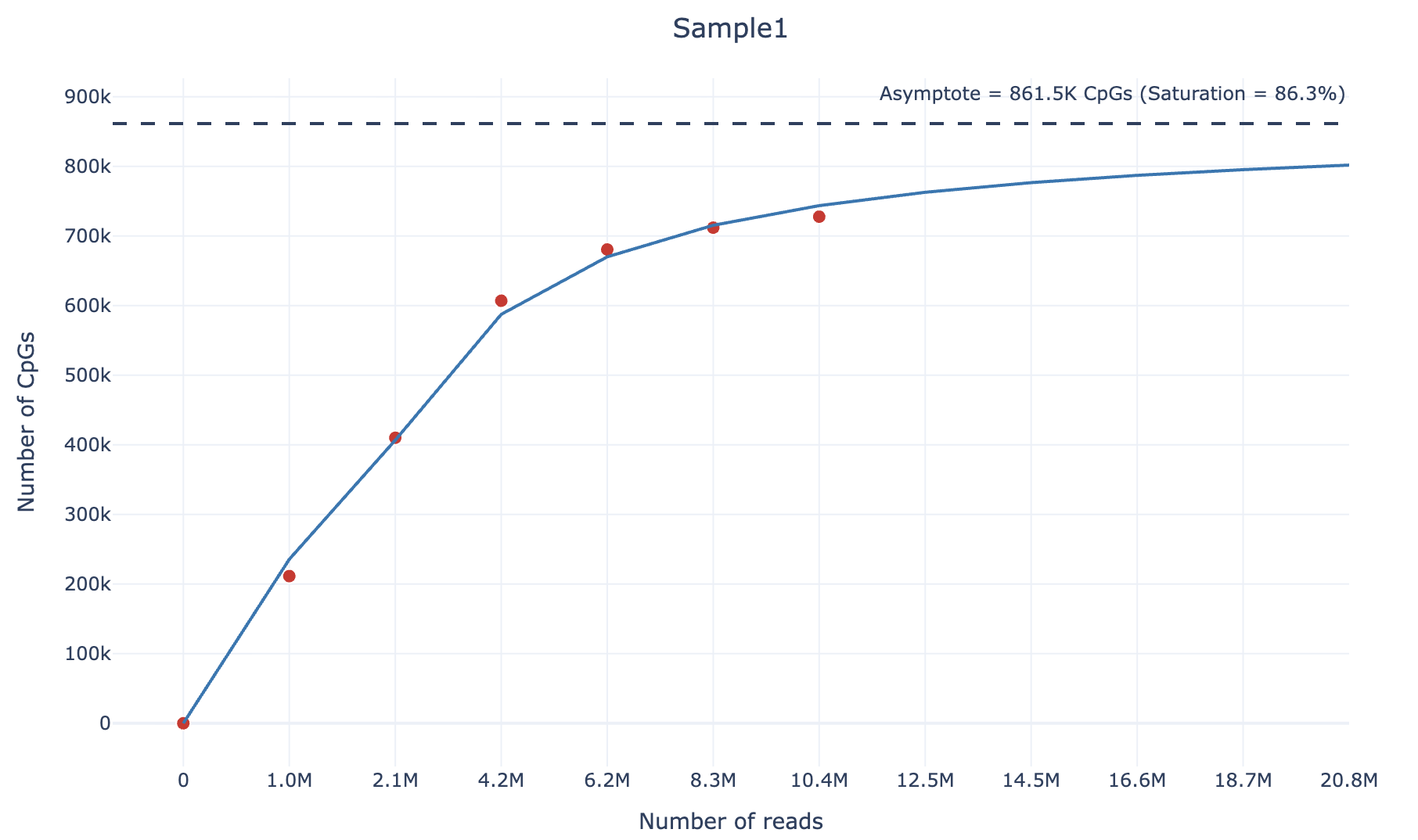
methurator plot --summary output/methurator_summary.ymlExample plot preview (also available as interactive html file here):
# Downsample BAM file
methurator downsample --genome hg19 my_sample.bam
# Generate plots from the results
methurator plot --summary output/methurator_summary.ymlThe output plots will be saved in output/plots/ as interactive HTML files showing the CpG predictions, the asymptote (theoretical maximum CpGs at t = 1000), the number of reads at each t, and confidence intervals (if enabled). The asymptote is now also used to compute the saturation values.
Example plot preview (also available as interactive html file here):
methurator gt-estimator uses an approach developed in 2018 by Chao Deng et al and further implemented in preseqR. This approach builds on the theoretical nonparametric empirical Bayes foundation of Good and Toulmin (1956), to model sequencing saturation and extrapolate to higher sequencing depths. The model implemented in preseqR was mirrored here and tailored toward sequencing saturation application. The workflow consists of the following steps:
- Extracts CpGs from BAM files using MethylDackel
- Fits the model implemented by Chao Deng et al taking in input the observed CpG counts
- Predicts future CpG discovery using rational function approximations
- Quantifies confidence intervals through bootstrap resampling (if enabled)
The extrapolation factor (t) represents the ratio of hypothetical total reads to actual observed reads. Values of t ≤ 1 correspond to interpolation (between observed data points), while t > 1 represents extrapolation (prediction beyond observed depth).
For a given coverage level:
- At t = 1: prediction matches observed CpGs, and the number of reads at full sequencing depth is reported in the summary file
- As t increases: predictions approach the theoretical asymptote (maximum CpGs at t = 1000, shown in the plot and used for saturation calculation)
To calculate the sequencing saturation of an DNAm sample when using the downsample command, we adopt the following strategy. For each sample, we downsample it according to 4 different percentages (default: 0.1,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8). Then, we compute the number of unique CpGs covered by at least 3 reads and the number of reads at each downsampling percentage.
We then fit the following curve using the scipy.optimize.curve_fit function:
We chose the arctangent function because it exhibits an asymptotic growth similar to sequencing saturation.
For large values of
Finally, the sequencing saturation value can be calculated as following:
This approach allows estimation of the theoretical maximum number of CpGs that can be detected given an infinite sequencing depth, and quantifies how close the sample is to reaching sequencing saturation.