This repository complements our TRO 2023 submission on FORESEE: Prediction with Expansion-Compression Unscented Transform for Online Policy Optimization with videos and plots.
Authors: Hardik Parwana and Dimitra Panagou, University of Michigan
Note: This repo is under development. While all the relevant code is present, we will work on making it more readable and customizable soon! Stay Tuned! Please raise an issue or send me an email if you run into issues before this documentation is ready. I am happy to help adapt this algorithm to suit your needs!
We propose a new method for numerical prediction of future states under generic stochastic dynamical systems, i.e, nonlinear dynamical systems with state-dependent disturbance. We use a sampling-based approach, namely Unscented Transform to do so. Previous approaches with UT only had state-independent uncertainty. The presence of state-dependent uncertainty necessiates to increase the number of samples, aka sigma points in UT, to grow with time. This leads to an unscalable approach. Therefore we propose Expansion-Contraction layers where
- Expansion Layer: maps each sigma point to multiple sigma points according to the disturbance level at that point. This leads to an increase in the total number of points.
- Compression Layer: uses moment matching to find a smaller number of sigma points that have the same moments as the expanded points A sequence of Expansion-Compression layer is used for multi-step prediction. Our layers are completely differentiable and hence can be used for policy optimization. Finally, we also propose an online gradient descent scheme for policy optimization.
| Constraint Satisfaction in Expectation | Constraint Satisfactyion with Confidence Interval |
|---|---|
 |
 |
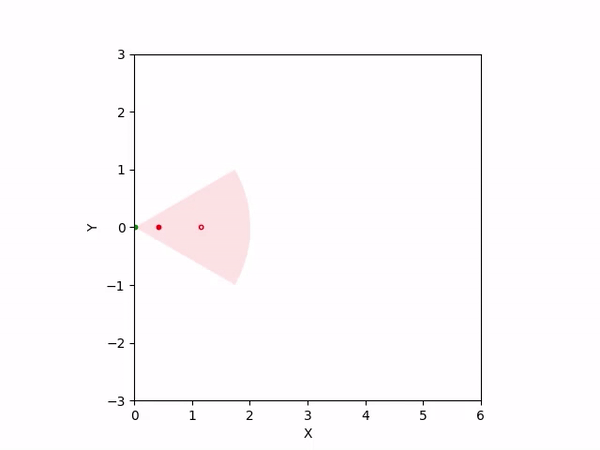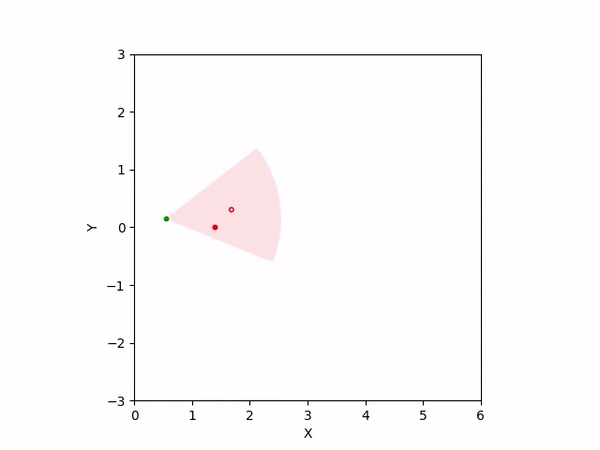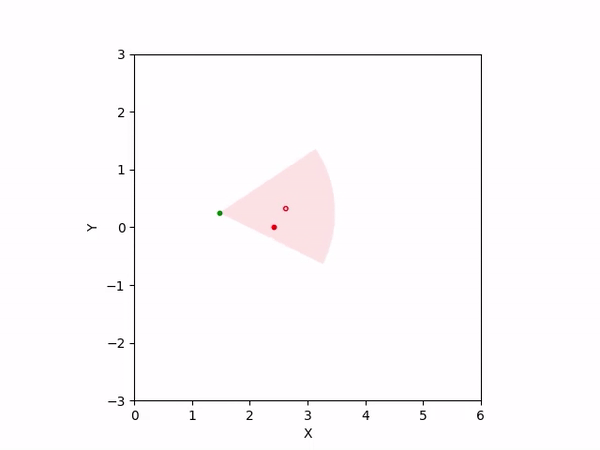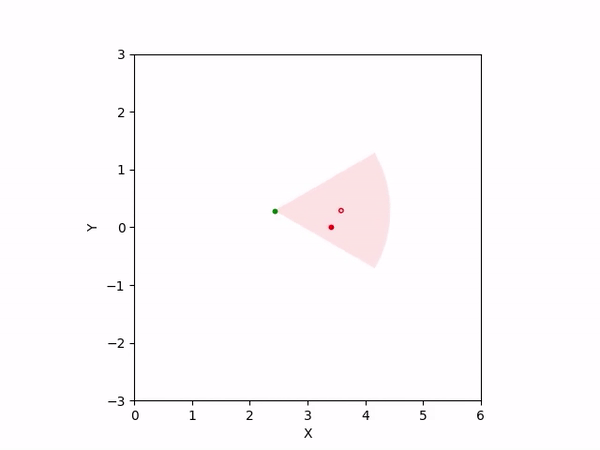
Th objective for the follower is to keep leader inside the field-of-view and, preferably, at the center. Adaptation is needed as depending on the pattern of leader's movement, different policy parameters perform better. The policy here is a CBF-CLF-QP that is to be satisfied in expectation when dynamics is uncertain. The first sim shows the performance of default parameters. The second one shows improvemwnt with our adaptation running online. Results change significantly when control input bounds are imposed. The QP does not even exhibit a solution after some time when default parameters are used and the simulation ends. The proposed algorithm is able toadapt parameters online to continuously satisfy input bounds. The prediction horizon is taken to be 20 time steps.
| No Adaptation | With adaptation | |
|---|---|---|
| No input bound | 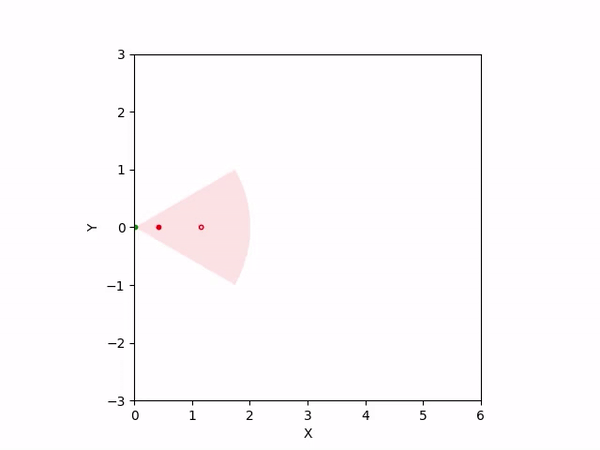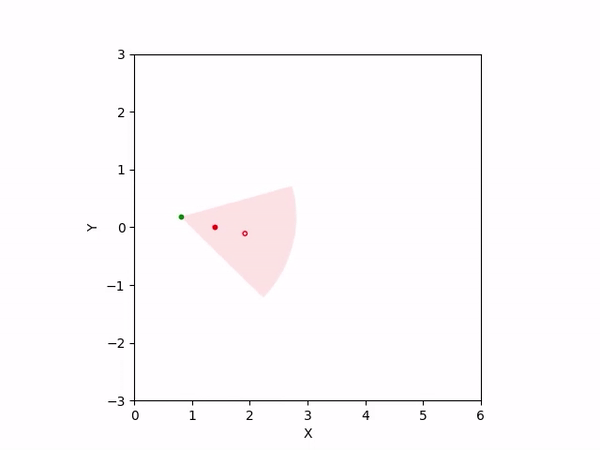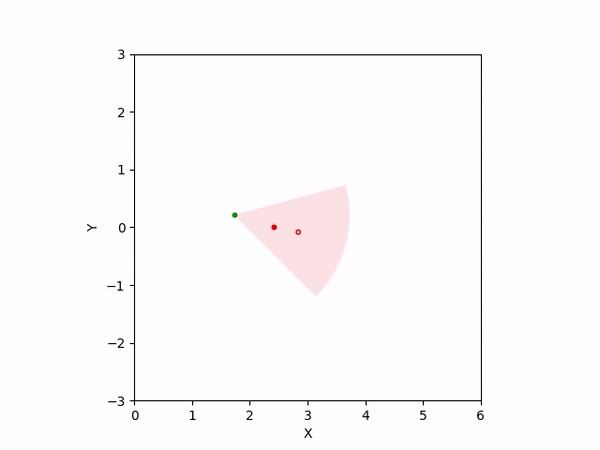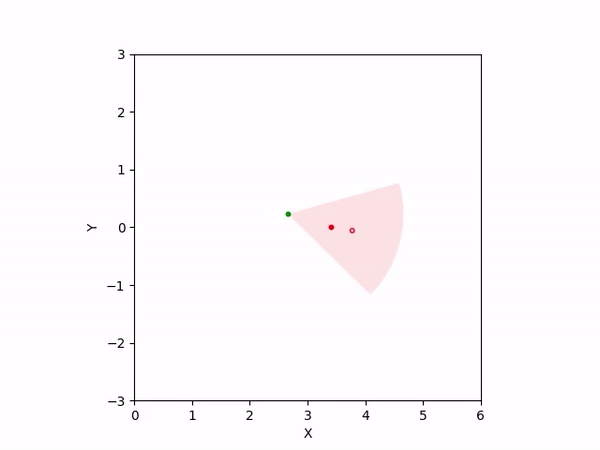 |
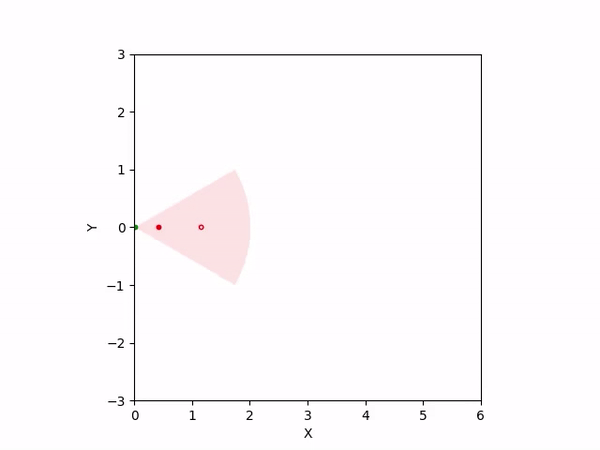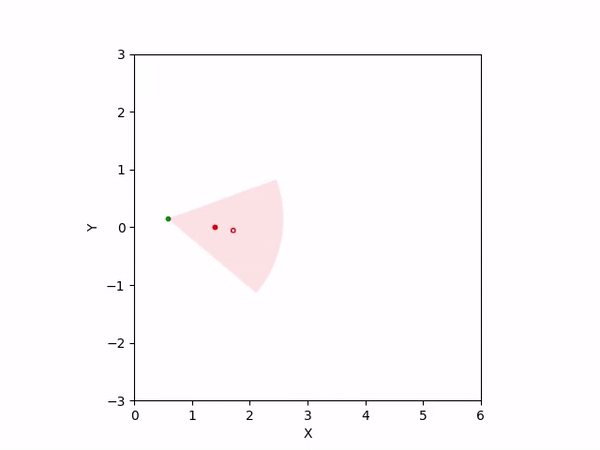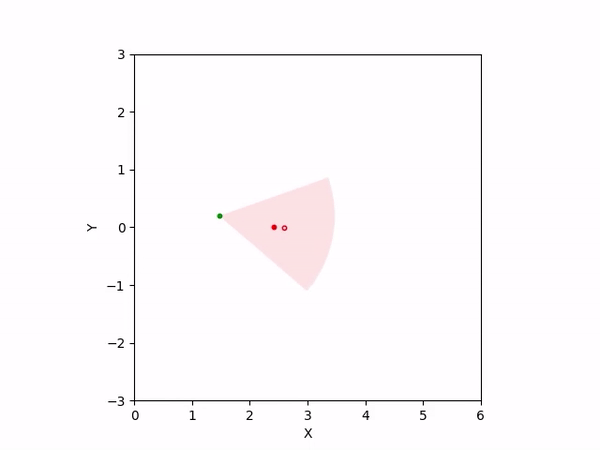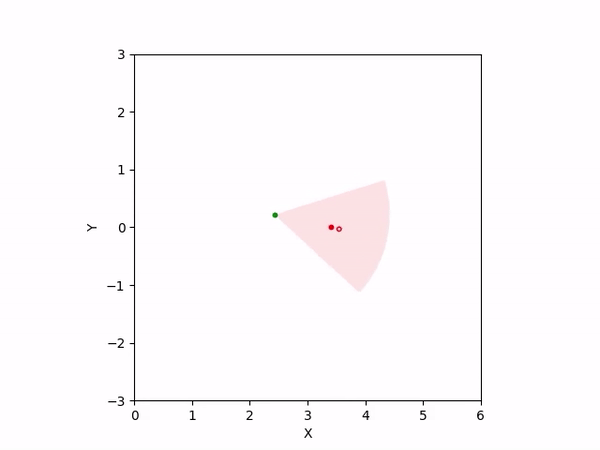 |
| With input bounds | 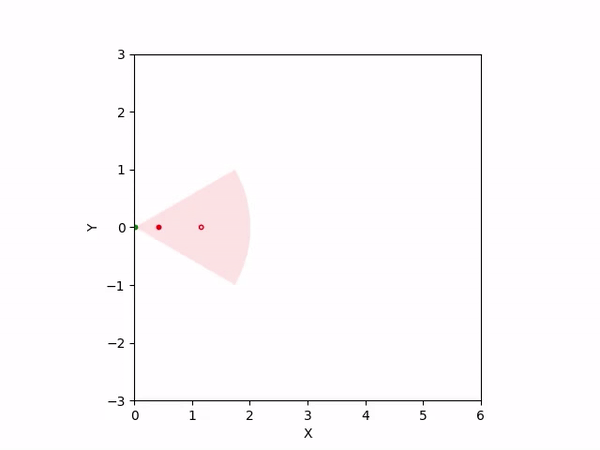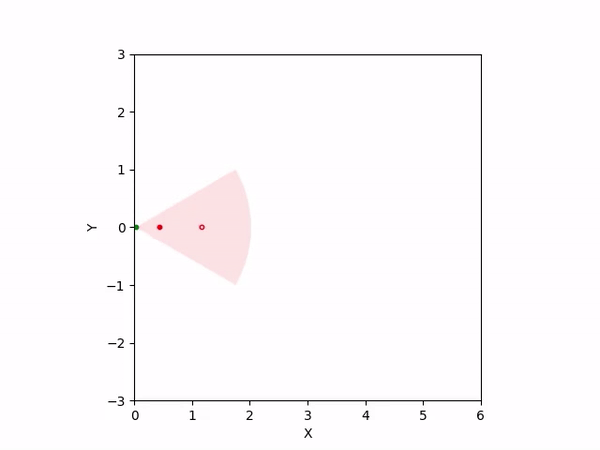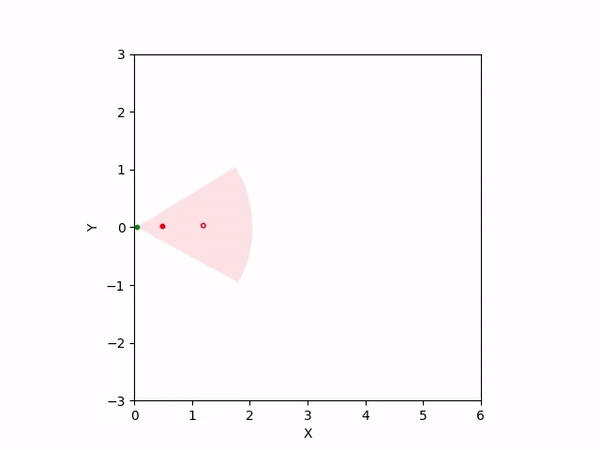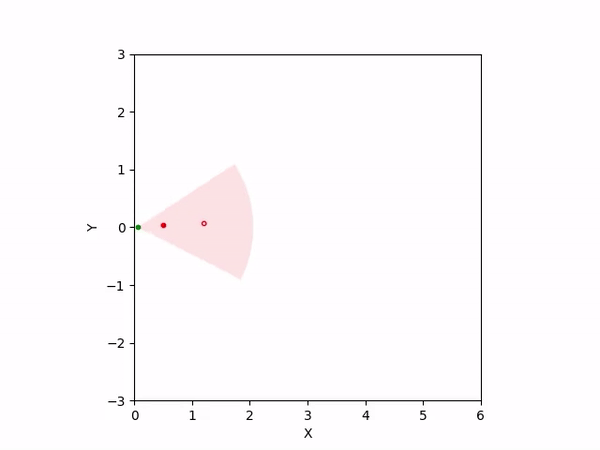 |
 |
Default parameters: https://youtu.be/G3gOAOpJPXM
Proposed: https://youtu.be/ibTU8vpVa34
For Pytorch code, the following dependencies are required:
- Python version 3.8
- numpy==1.22.3
- gym==0.26.0
- gym-notices==0.0.8
- gym-recording==0.0.1
- gpytorch==1.8.1
- torch==1.12.1 ( PyTorch's JIT feature was used to speed up computations wherever possible.)
- pygame==2.1.2
- gurobipy==9.5.1
- cvxpy==1.2.0
- cvxpylayers==0.1.5
- cartpole==0.0.1
For JAX code, the following dependencies are required
-
Python 3.11
-
numpy==1.22.3 matplotlib sympy argparse scipy==1.10.1
-
cvxpy==1.2.0 cvxpylayers==0.1.5 gym==0.26.0 gym-notices==0.0.8 gym-recording==0.0.1 moviepy==1.0.3 cyipopt==1.2.0 jax==0.4.13 jaxlib==0.4.11 gpjax==0.5.9 optax==0.1.4 jaxopt
-
diffrax==0.3.0
-
pygame==2.3.0
We also provide a Dockefile in the
docker_filesand 311_requirements.txt file for Python3.11 dependencies that can be used to run JAX examples
Note that you will also have to add a source directory to PYTHONPATH as there is no setup.py file provided yet. Note that the relevant gym environment for cartpole simulation is already part of this repo. This was done to change the discreet action space to a continuous action space and to change the physical properties of the objects.
We will be adding interactive jupyter notebooks soon! In the meantime, try out our scripts (comments to be addded soon!) To run the leader-follower example, run
python leader_follower/UT_RL_2agent_jit_simple.py
For cartpole, run
python cartpole/cartpole_UTRL_simple_offline_constrained.py
We aim to solve the following constrained model-based Reinforcement Learning(RL) problem.
Our approach involves following three steps:
- Future state and reward prediction using uncertain dyanmics model
- Compute Policy Gradient
- Peform Constrained Gradient Descent to update policy parameters
Step 1 and 2: The first two steps are known to be analytically intractable. A popular method, introduced in PILCO, computes analytical formulas for mean and covariance poropagation when the prior distribution is given by a Gaussian and the transition dynamics is given by a gaussian process with a gaussian kernel. We instead use Unscented Transform to propagate states to the future. Depending on number of soigma points employed, we can maintain mean and covariances or even higher order moments of the distribution. Propagting finite number of particles (sigma points) through state-dependent uncertainty model though requires increase in number of sigam points to be able to represent the distributions and this leads to an explosion that is undesirable. Therefore, we introduce differentiable sigma point expansion and compression layer based on moment matching that allows us to keep the algorithm scalable.
Step 3: We use Seqential Quadratic Programming type of update to use policy gradients in a way that help maintain constraints that were already satisfied by current policy. If current policy is unable to satisfy a constraint, then reward is designed to reduce the infeasibility margin of this unsatisfiable constraint.
In this example, we randomly initialize the parameters of the policy and then try to learn parameters online (in receding horizon fashion) that stabilize the pole in upright position. The policy used is taken from PILCO[1] Only a horizontal force on the cart can be applied. Only an uncertain dynamics model is available to the system. We run our algorithm for unconstrained as well as constrained cart position. The prediction horizon is taken to be 30 time steps.
- Unconstrained: X axis range (0,12) in animation
cartpole_unconstrained_h20-episode-0.mp4
- Constrained: X axis range (-1.5,1.5) in animation
cartpole_constrained_H20-episode-0.mp4
[1] Deisenroth, Marc, and Carl E. Rasmussen. "PILCO: A model-based and data-efficient approach to policy search." Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on machine learning (ICML-11). 2011.
