██████ ████ █████ ██████ █████ █████ ██████ █████ ████ ██████ █████ ██████ ██████
██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██
████ ██████ █████ ██ ██ ██ ████ ██ ████ ██ ██ ██ ███ ██████ ██
██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██ ██
██ ██ ██ █████ ██ █████ █████ ██ █████ ████ ██ █████ ██ ██It is a lightweight CLI app that uses llama.cpp to enable detection of AI generated text.
If you want to dig into the details of how it works, read the fast detect gpt paper
The original paper implementation uses PyTorch for inference, this project instead uses llama.cpp that leverages standard consumer hardware for faster performance.
This implementation follows the analytic Fast DetectGPT approach, which optimizes detection speed by utilizing a singular model for both sampling and scoring. Unlike previous methods (DetectGPT) that required separate steps or models, this approach combines the processes, necessitating only one model call per check. The core metric is the Conditional Probability Curvature, defined as:
Where:
-
$x$ -> The original input token -
$\log p_\theta(x)$ -> The log likelihood of the original token -
$\tilde{\mu}$ -> The average log likelihood of alternative samples generated by the model -
$\tilde{\sigma}$ -> The standard deviation of those sample log likelihoods
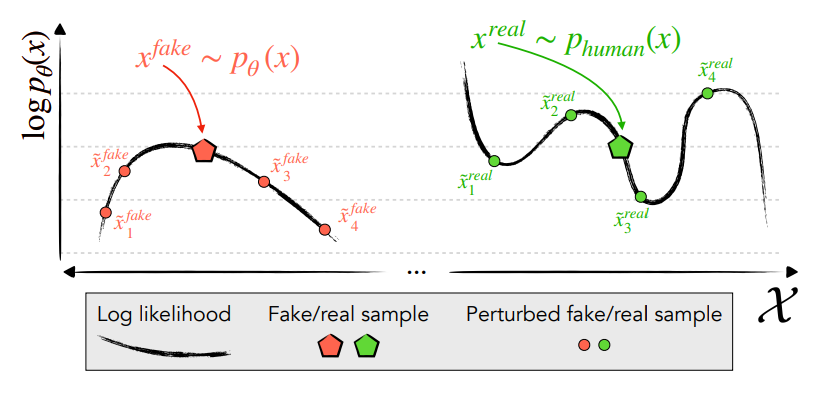
The algorithm assumes that AI generated text resides in the peaks of the model's probability curvature, as clearly
illustrated in the previous figure from the DetectGPT paper. Instead of relying on
computationally expensive sampling to
generate local neighbors, the analytical implementation directly evaluates the model's predictive distribution
for each token. By computing the theoretical expectation and variance of the conditional log probabilities, we obtain
an exact estimate of the local curvature.The metric normalizes the difference between the observed log likelihood and
its analytical expectation (
Next 2 steps are required!!
- install llama.cpp
- install arrow (in order to use parquet file as input)
cmake -B build .
cmake --build ./build --target fast-detect-gpt -j 6- create a .env file (you can use .env.sample as a template)
- Optional, if you don't have a model yet:
- get your huggingface token and set it in the .env file (https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/security-tokens)
- select the model huggingface url path in the .env file (default is for falcon-7b-instruct, suggested in the paper)
- If you have a model already downloaded, move it to the models/ folder or symlink it there, then set MODEL_NAME in the .env file to the folder name of the model
- move your input text file to the inputs/ folder and set INPUT_FILE in the .env file to the file name
- run:
-
bash ./run.sh
The output will be a discrepancy score for each input text, the higher the score the more likely it is that the text is human written.
You can compute the threshold that maximizes the F-Beta score on your train dataset using this script:
bash train.sh