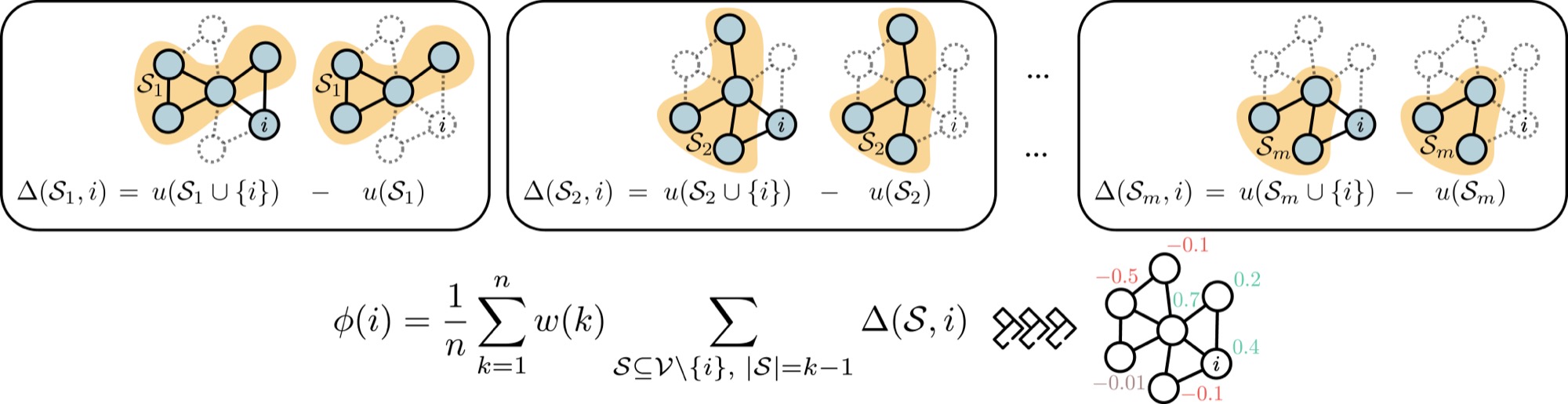
This repository contains the implementation of data valuation techniques for graph-structured data, as described in our paper Node-Level Data Valuation on Graphs.
git clone https://github.com/siantonelli/graph_valuation.git
cd graph_valuation
uv syncThe project automatically handles data and storage directories for you:
- Datasets will be automatically downloaded to
cfg.core.data_dir(defaults to./data/) when first needed - Results will be saved to
cfg.core.storage_dir(defaults to./storage/)
These directories are created automatically if they don't exist. You can customize these paths by modifying the configuration or setting environment variables. The default paths are relative to your project root directory.
This project uses Hydra for configuration management. Hydra enables you to compose your configuration dynamically and override any parameter from the command line. For more details on how Hydra works, visit hydra.cc.
The main script for computing node values is attribute_values.py. Here's a basic example:
uv run src/graph_valuation/scripts/attribute_values.py approach=training/banzhaf
train/model=sgc
train.n_models=1
dataset=cora_ml
data.data_seed=42
task.mode=transductive
approach.num_subsets=50000
approach.alpha=0.1
approach.setting=all
task.induced_subgraph=TrueDifferent data valuation methods can be used by changing the approach parameter. Available approaches are defined in conf/approach/training/:
banzhaf- Data Banzhaf valuationshapley- Data Shapley valuationloo- Leave-One-Out estimationdatamodel- DataModel approachpc_winter- PC-Winter valuation
Simply replace approach=training/banzhaf with any other approach from the configuration files.
Note: The inference pipeline (conf/approach/inference/) is currently work in progress (WIP). Use the training approaches for stable functionality.
You can also use the data valuation approaches programmatically in your Python code:
from pathlib import Path
import torch
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
from torch_geometric.datasets import CitationFull
import torch_geometric.transforms as T
from graph_valuation.approaches import DataBanzhaf, DataShapley, Datamodel
from graph_valuation.models import SGC
# Load dataset directly
pre_transform = T.Compose([
T.LargestConnectedComponents(),
T.ToUndirected()
])
transform = T.RandomNodeSplit(split="test_rest", num_val=140)
dataset = CitationFull(
root="data/cora_ml",
name="cora_ml",
pre_transform=pre_transform,
transform=transform
)
data = dataset[0]
# Configure training settings directly
train_cfg = OmegaConf.create({
"torch_device": None,
"device": "cpu",
"deterministic": True,
"n_models": 1,
"epochs": 3000,
"patience": 50,
"model_seed": 42,
"n_jobs": -1,
"model": {
"_target_": "graph_valuation.models.SGC",
"in_channels": data.num_features,
"out_channels": data.y.max().item() + 1
},
"optimizer": {
"_target_": "torch.optim.Adam",
"lr": 1e-2,
"betas": [0.9, 0.999],
"eps": 1e-08,
"weight_decay": 5e-4
}
})
# Set up results directory
results_dir = Path("storage/example_run")
results_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# Initialize a data valuation approach
valuator = DataBanzhaf(
filename="example_banzhaf",
n_subsets=1000, # Number of subsets to sample
alpha=0.1, # Subset size parameter
setting="all", # Which nodes to value: "all", "train"
induced_subgraph=True,
training_mode="transductive",
train_cfg=train_cfg,
results_dir=results_dir,
)
# Compute node values
print("Computing node values...")
nodes_values = valuator.attribute_values(
data=data,
utility_fn="margins", # Utility function: "margins", "test_accs", "val_accs"
learning_signal=True # Whether to use learning signal
)
print(f"Computed values for {len(node_values)} nodes")
print(f"Top 5 most valuable nodes: {node_values.argsort()[-5:]}")
# You can also use other approaches:
# DataShapley, Datamodel, LOO, PCWinter
# Each has slightly different parameters - see the approach files for detailsThe repository provides several experimental scripts to evaluate different aspects of data valuation methods.
For evaluating pre-computed node values, you first need to run attribute_values.py to generate the valuation results, then use the evaluation scripts.
Evaluate how well the computed values identify influential nodes by removing the most highly-valued nodes and measuring the impact on model performance:
uv run src/graph_valuation/scripts/evaluate_nodes_influence.py approach=training/banzhaf \
train/model=sgc \
train.n_models=1 \
dataset=cora_ml \
data.data_seed=42 \
task.mode=transductive \
approach.num_subsets=50000 \
approach.alpha=0.1 \
approach.setting=all \
task.induced_subgraph=TrueAssess the quality of computed values by measuring their predictive power for model behavior:
uv run src/graph_valuation/scripts/evaluate_predictive_supports.py approach=training/banzhaf \
train/model=sgc \
train.n_models=1 \
dataset=cora_ml \
data.data_seed=42 \
task.mode=transductive \
approach.num_subsets=50000 \
approach.alpha=0.1 \
approach.setting=all \
task.induced_subgraph=TrueNote: These evaluation scripts expect that you have already computed node values using the same configuration parameters.
The following experiments are standalone and compute their own valuations internally to measure specific characteristics of different approaches.
Evaluate different approaches using the Linear Datamodeling Score framework across various subset sizes and approximation parameters:
uv run src/graph_valuation/scripts/evaluate_lds.py '~approach' \
train/model=sgc \
train.n_models=1 \
dataset=cora_ml \
data.data_seed=42 \
task.mode=transductive \
+induced_subgraph=True \
+n_subsets=50000 \
+alpha=0.1 \
+p_trunc=0.25 \
+label_trunc_ratio=0 \
+group_trunc_ratio_hop_1=0.99 \
+group_trunc_ratio_hop_2=0.99 \
+setting=all \
+subset_sizes='[1000,2500,5000,10000,25000,50000]' \
+alphas='[0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 0.9]'Study memorization patterns across different valuation approaches using poisoned data detection:
uv run src/graph_valuation/scripts/run_memorization.py '~approach' \
train/model=sgc \
train.n_models=1 \
dataset=cora_ml \
data.data_seed=42 \
task.mode=transductive \
+poisoning_budget=0.1 \
+induced_subgraph=True \
+n_subsets=50000 \
+alpha=0.1 \
+p_trunc=0.25 \
+label_trunc_ratio=0 \
+group_trunc_ratio_hop_1=0.99 \
+group_trunc_ratio_hop_2=0.99 \
train.torch_device=cpu \
+high_logits=True \
+high_degree=FalseThe codebase is designed to be easily extensible for both custom models and data valuation approaches.
You can compute values for your own custom models by:
-
Creating a new model class in
src/graph_valuation/models/following the existing patterns (seegcn.py,sgc.py, etc.) -
Adding a corresponding Hydra configuration YAML file in
conf/train/model/ -
Important: Ensure your model's forward pass follows the standard PyTorch Geometric conventions. If not, you'll need to implement your own pipeline in the training functions (
training.py,inference.py)
You can implement your own data valuation methods by:
-
Creating a new approach class in
src/graph_valuation/approaches/following the existing patterns (see the various approach implementations) -
Adding a corresponding Hydra configuration YAML file in
conf/approach/training/orconf/approach/inference/depending on your approach type -
Key requirements for your custom approach:
- Inherit from the appropriate base class
- Implement the required methods for subset evaluation
- Handle the interaction with the training/inference pipeline
- Follow the expected input/output formats for compatibility with evaluation scripts
-
Important: Your approach should be compatible with the existing experiment framework to work with the evaluation and analysis scripts
If you need access to the specific datasets and experimental results used in our paper, please contact us at [antonelli at cs dot uni-koeln dot de]. We can provide guidance on obtaining the exact data configurations and pre-computed results that were used for the experiments described in the publication.
If you use this code in your research, please cite our paper:
@article{antonelli2025nodelevel,
title = {Node-Level Data Valuation on Graphs},
author = {Antonelli, Simone and Bojchevski, Aleksandar},
journal = {Transactions on Machine Learning Research},
issn = {2835-8856},
year = {2025},
url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=tNyApIqDSJ},
note = {},
}This project is licensed under the MIT License.