- The Coding Train
- The Nature of Code
- Games Fleadh
- Python
- Py5
- Processing
- Java
- https://github.com/maurymarkowitz/101-BASIC-Computer-Games
- MSX Online
- https://codingbat.com/python
- [Self enrole in this Brightspace](Creative Coding DMEDH1082: Sept-Dec Academic Term 2025/26)!
What you will need to install:
- Python
- Java
- VSCode
- Git
- py5
Course Notes:
- Python Introduction
- Py5
- Python Fundamentals
- Python OOP
- Notes on Processing sound
- OOP in Python 1
- OOP in Python 2
- OOP with Python & Py5
- Audio Examples
- Get the spaceship to shoot bullets. The bullets should have a lifetime of 10 5 seconds and should fade out. You can use a list to keep track of the bullets
- Create an asteroid class that floats around and wraps off the screen
- Have the asteroid disappear when hit by a bullet
- Submit your work on Brightspace!
Create these Audio Visualisers:
- Create a drum box, with square buttons. If you press inside thesquare, it plays a drum sound from the drums folder. Try to use a list in your solution
Playing and analysing sounddddddsss
Before you start, make sure you have:
-
Installed Py5:
pip install py5
-
Downloaded the Sound library:
import py5_tools py5_tools.processing.download_library("Sound")
-
Created your project folder:
my_lab/ ├── lab.py └── data/ └── (put your sound files here) -
Got some sound files (WAV or MP3 format) and placed them in the
datafolder
Objective: Load and play a sound file when you click the mouse.
What to do:
- Create a sketch that displays a message
- Load a sound file in
setup() - Play the sound when the user clicks the mouse
Hints:
- Import:
from processing.sound import SoundFile - Load with:
SoundFile(py5.get_current_sketch(), "filename.wav") - Use
mouse_pressed()function - Remember to use
globalfor your sound variable
Expected behavior: Click anywhere → sound plays!
Objective: Control the volume of a looping sound with mouse position.
What to do:
- Load a sound and make it loop continuously
- Use the mouse X position to control volume (left = quiet, right = loud)
- Display the current volume on screen
Hints:
- Use
soundfile.loop()to keep playing - Use
py5.remap()to convert mouse X to volume (0.0 to 1.0) - Update volume in
draw()with.amp(volume) - Show a visual bar to represent volume
Expected behavior: Moving mouse left/right changes volume smoothly!
Objective: Create a DJ speed controller using the mouse.
What to do:
- Load and loop a sound
- Use mouse Y position to control playback rate
- Top of screen = slow (0.5x), bottom = fast (2.0x)
- Display the current speed
Hints:
- Use
.rate()to change playback speed - Map mouse Y to rate range (0.5 to 2.0)
- Lower rates = deeper pitch, higher rates = higher pitch
- Show speed as text:
f"Speed: {rate:.2f}x"
Expected behavior: Moving mouse up/down changes pitch and speed!
Objective: Make sound move between left and right speakers.
What to do:
- Load and loop a sound
- Use mouse X to pan the sound from left speaker to right speaker
- Draw a circle that moves with the mouse to show panning position
Hints:
- Use
.pan()with values from -1.0 (left) to 1.0 (right) - Map mouse X to pan range
- Draw a circle at mouse X position
- Label left and right sides of screen
Expected behavior: Sound follows your mouse from speaker to speaker!
Objective: Create a circle that grows and shrinks with the music's volume.
What to do:
- Load and loop a sound
- Create an Amplitude analyzer
- Draw a circle that gets bigger when the music is loud
- Change the circle's color based on volume
Hints:
- Import and use
Amplitudeclass - Create analyzer:
amplitude = Amplitude(py5.get_current_sketch()) - Connect to sound:
amplitude.input(soundfile) - Get value:
amp = amplitude.analyze() - Map amp (0.0-0.5 range) to circle size
Expected behavior: Circle pulses with the beat!
Objective: Create a basic spectrum analyzer with colored bars.
What to do:
- Load and loop a sound
- Create an FFT analyzer with 64 bands
- Draw 64 rectangles across the screen
- Each bar's height represents that frequency's amplitude
- Color the bars from red (low) to blue (high)
Hints:
- Import and use
FFTclass - Create:
fft = FFT(py5.get_current_sketch(), 64) - Analyze each frame:
fft.analyze() - Loop through bands:
for i in range(64) - Get amplitude:
fft.spectrum[i] - Bar width = screen width / number of bands
Expected behavior: Colorful bars dance to the music!
Objective: Improve your spectrum analyzer with smooth animation.
What to do:
- Take your Exercise 6 code
- Add smoothing so bars don't jump around
- Make bars fade down slowly instead of instantly
Hints:
- Create a list to store smoothed values:
sum_values = [0.0] * bands - Use smoothing formula:
sum_values[i] += (fft.spectrum[i] - sum_values[i]) * 0.2 - The 0.2 is the smoothing factor (smaller = smoother)
- Draw using
sum_values[i]instead of rawfft.spectrum[i]
Expected behavior: Bars move smoothly and look professional!
Objective: Generate a pure tone using a sine wave oscillator.
What to do:
- Create a sine wave oscillator
- Set it to play the note A (440 Hz)
- Press SPACE to start/stop the tone
- Display "Playing" or "Stopped" status
Hints:
- Import and use
SinOscclass - Set frequency:
.freq(440) - Set volume:
.amp(0.5) - Toggle with
.play()and.stop() - Track state with a boolean variable
Expected behavior: Press SPACE → hear a pure tone!
Objective: Create a playable piano with 8 notes.
What to do:
- Create 8 sine wave oscillators
- Map keys A, S, D, F, G, H, J, K to musical notes
- Play note when key pressed, stop when released
- Draw 8 rectangles as piano keys
- Highlight key when pressed
Hints:
- Note frequencies: C=261.63, D=293.66, E=329.63, F=349.23, G=392.00, A=440.00, B=493.88, C=523.25
- Use
key_pressed()andkey_released() - Use a dictionary or list to store oscillators
- Draw keys in different colors when active
Expected behavior: Play music with your keyboard!
Objective: Play musical chords with three oscillators.
What to do:
- Create 3 sine wave oscillators
- Press '1' for C Major chord (C, E, G)
- Press '2' for D Minor chord (D, F, A)
- Press '3' for G Major chord (G, B, D)
- All three notes play together
Hints:
- C Major: 261.63 Hz, 329.63 Hz, 392.00 Hz
- D Minor: 293.66 Hz, 349.23 Hz, 440.00 Hz
- G Major: 392.00 Hz, 493.88 Hz, 587.33 Hz
- Start all 3 oscillators in
key_pressed() - Stop all 3 in
key_released()
Expected behavior: Press keys to play harmonious chords!
Objective: Apply a low-pass filter that you can control in real-time.
What to do:
- Load and loop a sound
- Add a low-pass filter
- Control filter frequency with mouse X
- Show the cutoff frequency on screen
- Low frequencies = left, high frequencies = right
Hints:
- Import and use
LowPassclass - Create:
lowpass = LowPass(py5.get_current_sketch()) - Connect:
lowpass.process(soundfile) - Control:
lowpass.freq(cutoff) - Map mouse X to range 100-10000 Hz
Expected behavior: Left = muffled, right = clear!
Objective: Create an echo/delay effect controller.
What to do:
- Load and loop a sound
- Add a delay effect
- Use mouse X to control delay time (0 to 2 seconds)
- Use mouse Y to control feedback amount (0.0 to 0.9)
- Display both values
Hints:
- Import and use
Delayclass - Set time:
.time(seconds) - Set feedback:
.feedback(amount) - Don't go above 0.9 feedback or it gets crazy!
- Show visual feedback bars
Expected behavior: Create echo effects by moving the mouse!
Objective: Visualize sound from your microphone in real-time.
What to do:
- Capture audio from the microphone
- Use amplitude analyzer to get volume level
- Draw a meter that shows how loud you are
- Change color based on volume (green = quiet, red = loud)
Hints:
- Import and use
AudioInandAmplitude - Create:
mic = AudioIn(py5.get_current_sketch(), 0) - Start:
mic.start() - Connect amplitude analyzer to mic input
- Map amplitude to bar height and color
Expected behavior: Talk/sing into mic → see visual feedback!
Objective: Create a live spectrum analyzer for microphone input.
What to do:
- Capture microphone audio
- Use FFT to analyze frequencies
- Draw spectrum bars showing what frequencies you're making
- Try singing different notes and see them light up!
Hints:
- Combine microphone input with FFT analyzer
- Use fewer bands (64 or 128) for better performance
- Map frequency bands to bar positions
- Low frequencies on left, high on right
Expected behavior: Whistle high notes → right side lights up!
Objective: Combine everything you've learned into one awesome visualizer!
What to do:
- Load and loop a music file
- Create FFT spectrum bars (colorful!)
- Add a pulsing center circle (amplitude)
- Make the background brightness pulse with the music
- Add smooth animations
Hints:
- Use both FFT and Amplitude analyzers
- Use smoothing on spectrum values
- Map amplitude to background color
- Use
py5.color_mode(py5.HSB)for rainbow colors - Add your own creative touches!
Objective: Create a theremin-like instrument controlled by mouse position.
What to do:
- Use mouse X for pitch (frequency)
- Use mouse Y for volume
- Only play when mouse is pressed
- Show frequency and volume values
- Add visual elements (waveform display?)
Hints:
- Use a sine or triangle oscillator
- Map X to wide frequency range (100-2000 Hz)
- Map Y to volume (0.0-0.8)
- Start oscillator on mouse press
- Stop on mouse release
Expected behavior: Wave your mouse around to make music!
If no sound plays:
- Check your sound file is in the
datafolder - Check the filename spelling is exactly right
- Make sure you called
.play()or.loop() - Check your computer's volume is up
Once you've completed the exercises, try these:
- Visualize different songs - See how different genres look
- Add mouse click effects - Trigger sounds with clicks
- Create transitions - Fade between different effects
- Make it full screen - Use
py5.full_screen() - Add recording - Save your visualizations as videos
- Combine exercises - Mix multiple concepts together
- Create a game - Add sound to a simple game
- Build a DJ controller - Multiple sounds + effects
- Py5 Documentation: https://py5coding.org
- Processing Sound Reference: https://processing.org/reference/libraries/sound/
- Free Sound Files: freesound.org, zapsplat.com
- Audio Conversion: Use Audacity (free) to convert sound formats
When you complete exercises:
- Take screenshots of your visualizers
- Record short videos of your instruments
- Share your code with the class on discord
Create a variable with a player name and practice string manipulation:
- Store a player name like "SHADOWHUNTER_99"
- Convert it to lowercase
- Extract just the username part (before the underscore)
- Create a welcome message using f-strings: "Welcome, {username}!"
Create a long dialogue string from a game NPC:
dialogue = "Greetings, traveler! I have a quest for you. Find the ancient sword in the dark forest."- Use slicing to extract just the first sentence
- Get the last 20 characters
- Extract every second character (step slicing)
- Find the word "quest" using string methods
Game cheat codes often need to be processed:
- Create a cheat code string: "POWERUP_HEALTH_MAX"
- Use
split()to break it into parts - Use
replace()to change underscores to spaces - Practice slicing to get the first word, last word, and middle word
Create a basic inventory using lists:
- Make a list of 5 items:
["sword", "potion", "shield", "key", "map"] - Add a new item to the inventory
- Remove an item the player used
- Check if a specific item is in the inventory
- Print how many items the player has
Create a list of enemy types and manipulate it:
- Start with:
enemies = ["goblin", "orc", "troll"] - Add a boss enemy at the end
- Insert a new enemy type at position 1
- Create a slice of the first 2 enemies
- Reverse the list to change spawn order
- Make a copy of the list for a second level
Work with a list of numbers representing scores:
- Create a list:
scores = [1500, 2300, 1800, 3200, 2100] - Find the highest score using
max() - Find the lowest score
- Sort the scores in descending order
- Get the top 3 scores using slicing
- Calculate the average score
Create a dictionary to store player attributes:
player = {
"name": "Hero",
"health": 100,
"mana": 50,
"level": 1
}- Access and print the player's health
- Update the health after taking damage
- Add a new stat like "experience"
- Print all the stat names (keys)
- Print all the values
Create a dictionary of game items with their properties:
items = {
"sword": {"damage": 15, "type": "weapon"},
"potion": {"healing": 25, "type": "consumable"},
"shield": {"defense": 10, "type": "armor"}
}- Access the damage value of the sword
- Add a new item with its properties
- Print all item names
- Check if "potion" exists in the items
- Update the shield's defense value
Create a settings dictionary:
settings = {
"difficulty": "normal",
"sound_volume": 75,
"music_on": True,
"controls": ["W", "A", "S", "D"]
}- Change the difficulty to "hard"
- Adjust the volume
- Access the control keys and print just the first two
- Add a new setting for screen resolution
Use a list to draw multiple coins on screen:
def setup():
size(600, 400)
def draw():
background(220)
coin_positions = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
for x in coin_positions:
fill(255, 215, 0)
circle(x, 200, 30)- Run this code
- Add y-coordinates by making it a list of lists:
[[100, 200], [200, 150], ...] - Modify to draw coins at different positions
Use slicing and dictionaries to create a health bar:
player_stats = {
"health": 75,
"max_health": 100
}
def setup():
size(400, 200)
def draw():
background(50)
# Health bar
bar_width = 300
current_width = (player_stats["health"] / player_stats["max_health"]) * bar_width
# Background bar
fill(100)
rect(50, 50, bar_width, 30)
# Health bar (changes color based on health)
if player_stats["health"] > 50:
fill(0, 255, 0) # Green
elif player_stats["health"] > 25:
fill(255, 255, 0) # Yellow
else:
fill(255, 0, 0) # Red
rect(50, 50, current_width, 30)- Experiment with different health values
- Add a text label showing the health numbers
Create a system that spawns enemies in waves using lists and dictionaries:
current_wave = 0
waves = [
{"enemies": ["goblin", "goblin"], "count": 2},
{"enemies": ["goblin", "orc", "goblin"], "count": 3},
{"enemies": ["orc", "orc", "troll"], "count": 3}
]
def setup():
size(600, 400)
text_size(16)
def draw():
background(220)
# Display current wave info
wave_data = waves[current_wave]
fill(0)
text(f"Wave {current_wave + 1}", 20, 30)
text(f"Enemies: {wave_data['count']}", 20, 50)
# Display enemy types
y_pos = 80
for i, enemy in enumerate(wave_data['enemies']):
text(f"{i+1}. {enemy}", 20, y_pos)
y_pos += 25
run()- Modify the code to add a 4th wave
- Add a "boss" property to wave dictionaries (True/False)
- Display boss waves differently
Create a visual inventory grid using nested lists:
inventory_grid = [
["sword", "potion", None],
["shield", None, "key"],
[None, "map", "coin"]
]
def setup():
size(400, 400)
def draw():
background(200)
cell_size = 100
for row in range(3):
for col in range(3):
x = col * cell_size + 50
y = row * cell_size + 50
# Draw cell
fill(255)
stroke(0)
rect(x, y, 80, 80)
# Draw item if exists
item = inventory_grid[row][col]
if item:
fill(0)
text_align(CENTER, CENTER)
text(item, x + 40, y + 40)
run()- Add more items to the grid
- Change the grid to 4x4
- Add color coding for different item types
Combine everything into a complete player profile:
player_profile = {
"username": "DragonSlayer_42",
"stats": {"health": 100, "mana": 80, "stamina": 60},
"inventory": ["sword", "potion", "shield"],
"quest_log": ["Find the ancient tome", "Defeat 10 goblins"],
"achievements": ["First Blood", "Survivor"]
}- Access and print just the username (without the number)
- Add a new item to inventory
- Mark a quest as complete by removing it
- Add a new achievement
- Calculate total stat points
- Create a formatted status report that prints all information nicely
Create a random loot system using lists and dictionaries. Items should have rarity levels.
Build a branching dialogue system using nested dictionaries where each choice leads to different responses.
Create a leaderboard system that stores player names and scores in a list of dictionaries, then sorts them by score.
Form a group. Go out into the campus and take pictures of patterns you find in nature and the environment around you
Share on discord
Use loops and Py5 to create artistic interpretations of things that you find
Combine your sketches with those of your team mates and make a collage
Share your creations on discord. Upload the code and some screenshots to brightspace to get your mark for this week
Draw these:
Variables exercises:
If statement Exercises:
-
Check out these music visualisers made in Processing by previous programming students
-
If you are curious, check out some of my creature videos
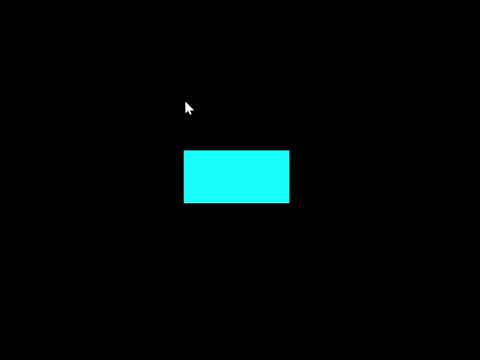
Write a sketch to draw the following shape: