Installation | Examples | Docs | Acknowledge | Citation
Based on the important perspective that time series are external manifestations of complex dynamical systems,
we propose a bimodal generative mechanism for time series data that integrates both symbolic and series modalities.
This mechanism enables the unrestricted generation of a vast number of complex systems represented as symbolic expressions
[Sep. 2025] Our paper "Synthetic Series-Symbol Data Generation for Time Series Foundation Models" has been accepted by NeurIPS 2025, where SymTime pre-trained on the
We have highly encapsulated the algorithm and uploaded the code to PyPI. Users can download the code through pip.
pip install s2generator
We only used NumPy, Scipy and matplotlib when developing the project.
We provide a unified data generation interface Generator, two parameter modules SeriesParams and SymbolParams, as well as auxiliary modules for the generation of excitation time series and complex system. We first specify the parameters or use the default parameters to create parameter objects, and then pass them into our Generator respectively. finally, we can start data generation through the run method after instantiation.
import numpy as np
# Importing data generators object
from S2Generator import Generator, SeriesParams, SymbolParams, plot_series
# Creating a random number object
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
# Create the parameter control modules
series_params = SeriesParams()
symbol_params = SymbolParams() # specify specific parameters here or use the default parameters
# Create an instance
generator = Generator(series_params=series_params, symbol_params=symbol_params)
# Start generating symbolic expressions, sampling and generating series
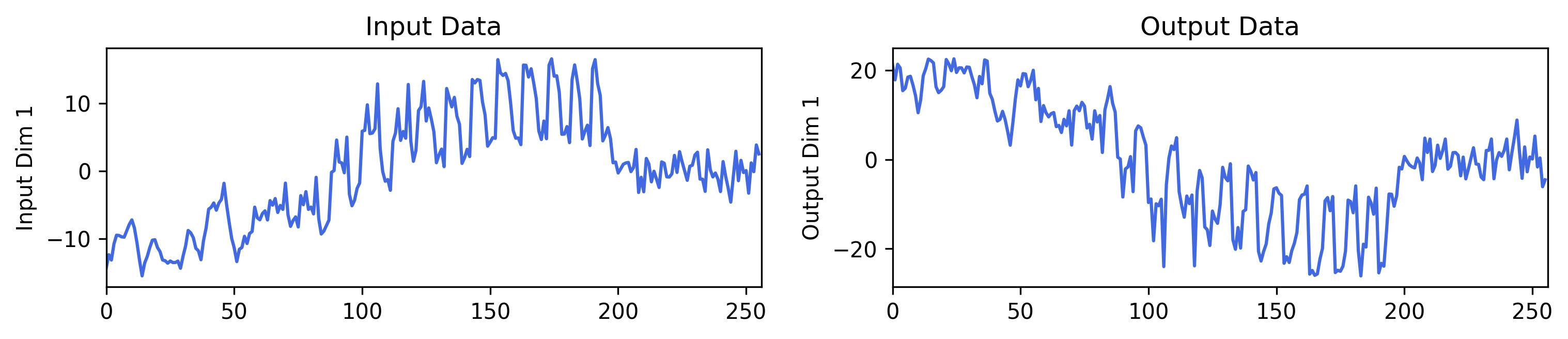
symbols, inputs, outputs = generator.run(
rng, input_dimension=1, output_dimension=1, n_inputs_points=256
)
# Print the expressions
print(symbols)
# Visualize the time series
fig = plot_series(inputs, outputs)(73.5 add (x_0 mul (((9.38 mul cos((-0.092 add (-6.12 mul x_0)))) add (87.1 mul arctan((-0.965 add (0.973 mul rand))))) sub (8.89 mul exp(((4.49 mul log((-29.3 add (-86.2 mul x_0)))) add (-2.57 mul ((51.3 add (-55.6 mul x_0)))**2)))))))
The input and output dimensions of the multivariate time series and the length of the sampling sequence can be adjusted in the run method.
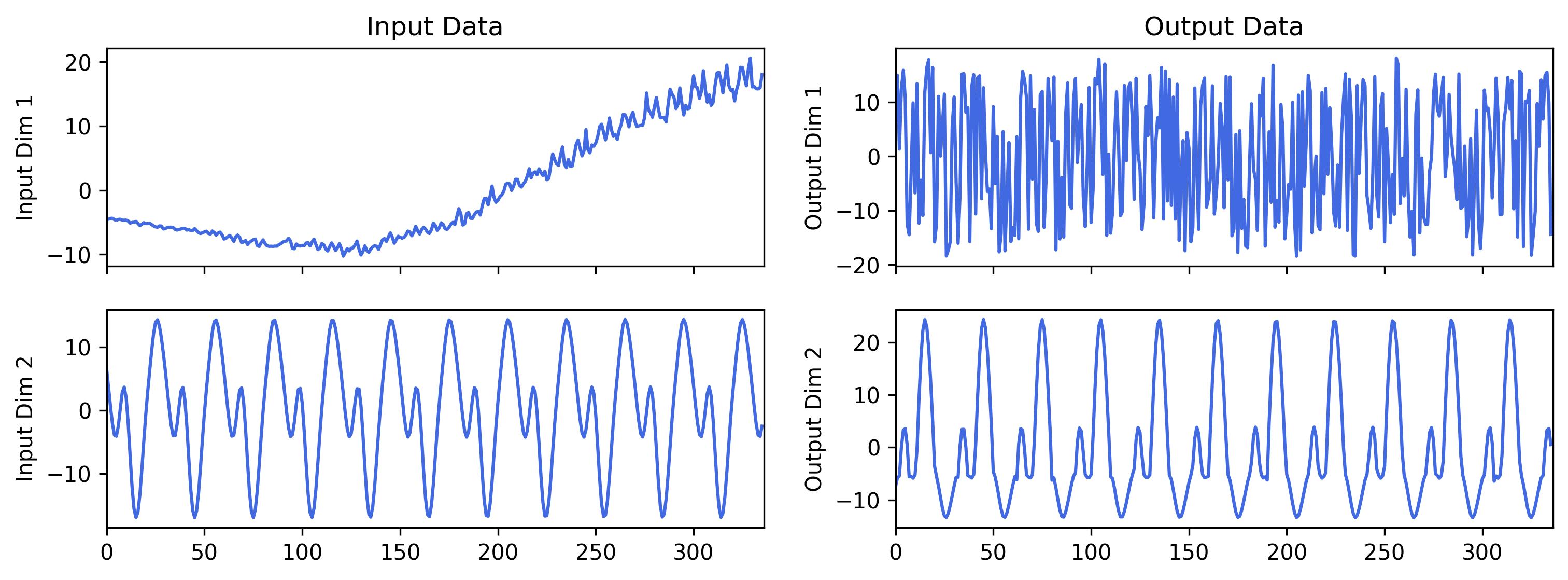
rng = np.random.RandomState(512) # Change the random seed
# Try to generate the multi-channels time series
symbols, inputs, outputs = generator.run(rng, input_dimension=2, output_dimension=2, n_inputs_points=336)
print(symbols)
fig = plot_series(inputs, outputs)(-9.45 add ((((0.026 mul rand) sub (-62.7 mul cos((4.79 add (-6.69 mul x_1))))) add (-0.982 mul sqrt((4.2 add (-0.14 mul x_0))))) sub (0.683 mul x_1))) | (67.6 add ((-9.0 mul x_1) add (2.15 mul sqrt((0.867 add (-92.1 mul x_1))))))
Two symbolic expressions are connected by " | ".
The advantage of
MixedDistribution: Sampling from a mixture of distributions can show the random of time series;ARMA: The sliding average and autoregressive processes can show obvious temporal dependencies;ForecastPFNandKernelSynth: The decomposition and combination methods can reflect the dynamics of time series;IntrinsicModeFunction: The excitation generated by the modal combination method has obvious periodicity.
By generating diverse complex systems and combining multiple excitation generation methods, we can obtain high-quality, diverse time series data without any constraints. For detailed on the data generation process, please refer to our paper or documentation.
If you find this
@misc{wang2025syntheticseriessymboldatageneration,
title={Synthetic Series-Symbol Data Generation for Time Series Foundation Models},
author={Wenxuan Wang and Kai Wu and Yujian Betterest Li and Dan Wang and Xiaoyu Zhang},
year={2025},
eprint={2510.08445},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.08445},
}